Cell Biology and Biochemistry Workbook
How to complete this workbook:
Work through each answer in the workbook as you go. If you run out of space, simply use one of the additional sheets to record your answer. Remember to add your name and the question number.
Remember to show your working out for each question!
You MUST answer ALL of the questions.
1
Access to Higher Education
Diploma Nursing & Midwifery
|
Q1 |
Describe the differences between a Prokaryotic cell and a Eukaryotic cell. On the basis of cellular structure all living organism are categorized into two categories that is prokaryotic and eukaryotic. There are following differences in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||
|
1.1 |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Mark: |
|
Q2 |
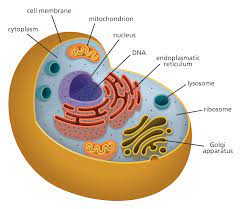
Label the following diagram;
|
|
|
1.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q3 |
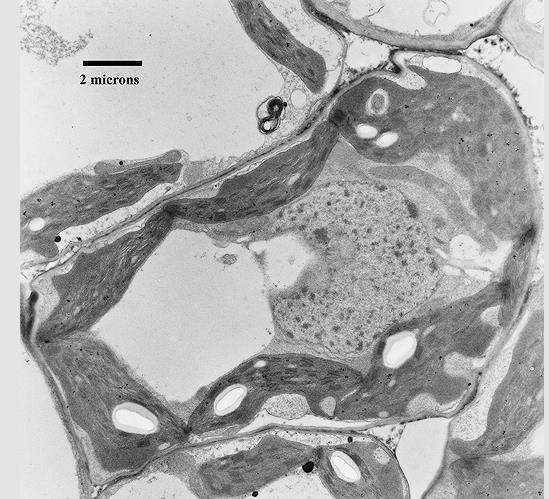
How large is the following cell?
|
2000 nm |
|
1.2 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q4 |
How large is the following organelle?
|
0.2 micron to 0.5 micron |
|
1.2 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q5 |
Complete the following chart;
|
|
|
1.3 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q6 |
Identify the following tissue. What are the key specialist features of the cells in this tissue and how do they work together? This diagram is belongs to the epidermis layer of skin. In which five layers of cells are present. (1) Stratum basal cell is made up of basal cells, which is a cuboid shaped stem cells which is the precursor of keratinocytes of the epidermis. It constantly going to mitosis and help to produce new cells.(2) Stratum spinosum is spiny appearance because of the protruding cell process which help to join the cells through a structure known as Desmosomes. It provides the strength between the cells. Keratinocytes in the stratum spinosum start the synthesis of keratin protein and release the glycolipid which has water repelling property and prevent water loss from the body. (3) Stratum granulosum cells has granule like appearance. It also help to prevent the water loss prom the body by making an waterproof barrier. (4)stratum Lucidum: It is the translucent layer of skin made of dead keratinocytes it also provide a barrier to waterand it is very rich protein layer. (5) stratum corneum:it is superficial layer of skin and exposed to outside the environment. It is dead and dry cells layers which help to prevent the entry of microbes and prevent the dehydration process. Also provides the mechanical protection against the erosion. These all layers of skin cells together perform the function like protection, prevent dehydration, provide strength to the skin which help to protect against outer abrashion . |
|
|
1.3 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q7 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
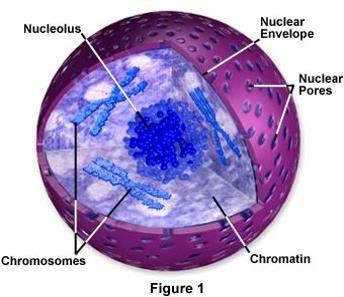
The organelles which shows in the figure is nucleus. It help to control and regulate the cells activities that is growth and metabolism. It carries gene, which contain the heredity information. Nucleus contains nucleoplasm which contains the cell's genetic material and genetic material of the cells organized as DNA molecules. DNA molecules have variety of protein which help to form chromosome. Genetic materials of the cells relate all the functions which is done by the cells. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
Related Services: Phd Dissertation Help
|
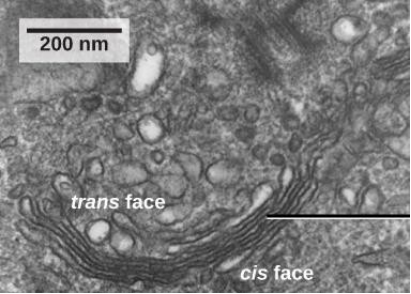
Q8 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
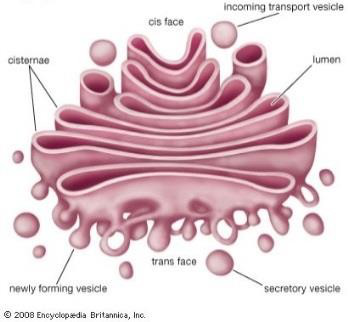
The above mentioned organelle is known as Golgi apparatus. Functions of Golgi apparatus are: Modification of protein and lipids. Removal of process materials from the cells. Formation and secretion of mucus. Packaging and transportation of product into the vesicles. It is central intracellular membrane-bound organelle which key function in trafficking, processing, and sorting of newly synthesized membrane and secretory proteins and lipids. To provide best function, Golgi membranes have a unique stalked structure. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q9 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
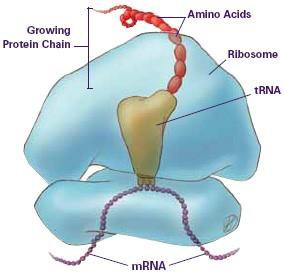
ANS: This is Ribosomal picture. This responsible for synthesis of protein for the cell via mRNA through the process of translation. Grooves of the robosomes allow for mRNA to be held in place while tRNA helps to reads the “code” which indicate that which amino acid is next in the sequence. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
Students Also Read: Network Diagram sample
|
Q10 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
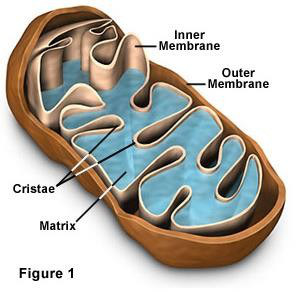
Ans: This is mitochondrial structure. It is known as powerhouse of the cell because it help to produce ATP. The folding of the internal membrane enhances the surface area inside the organelle. Therefore, most of the chemical reaction occur inside the membrane, the large surface area makes more space for the reactions to occur. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q11 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
This organelles is named as lysosome. The main function of lysosomes are: digestion of macro molecules. Cell membrane repair work. Digestion of foreign particles. Lysosomes are a round shaped sacs which is filled with hydrolytic enzyme which have capabilities to break down the macromolecules. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
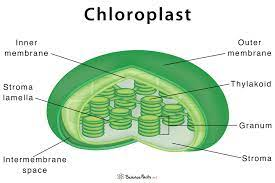
Q12 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
This is the structure of chloroplast. It help to convert light energy into stable chemical energy through the photosynthetic process. It also provides diverse metabolic activities for plant and also participate in the synthesis of fatty acid, and membrane lipids. Chloroplast have structure known as chlorophyll which trap the solar energy and use in the synthesis of food. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
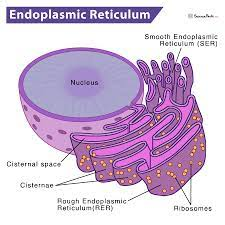
Q13 |
What is this organelle? What is it’s function? How does it’s structure help it function?
The above organelle is Endoplasmic reticulum. Function: store calcium. protein synthesis. Lipid metabolism. ER have dynamic structure that play many roles in the cell. The different function of the ER are perform through the clear domains like consisting of tubules, nuclear envelope and sheets. |
|
|
2.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
Q14 |
Match the correct molecule to the structure;
Protein Fat Carbohydrate Ans: (1)- carbohydrates (2)- protein (3)- Fat |
|
|
3.1 |
||
|
Mark: |
|
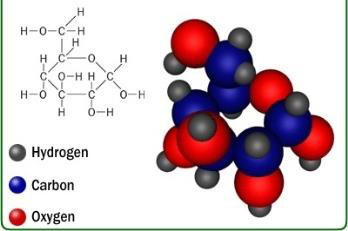
Q15 |
Compare the differences in structure between Carbohydrates, Lipids and Proteins and explain how their different structures help them function. Ans: lipid and carbohydrate molecules have only carbon,hydrogen and oxygen molecules in their structure where as proteins molecule three extra elements like nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus in its structure. The protein molecules assist as the transport channels of the molecules. Carbohydrate work as receptors which analyze the signals outside from the cells. Lipid provides protective barriers for molecule in structure. |
|
|
3.1 |
||
|
Mark 9 |
|
Q16 |
Explain the formation and breakdown of polymers. Ans: Formation process occur by two process which is (1) addition- addition of monomer by the catalyst. (2) condensations- addition of monomers by the help of exposed hydrogen bond. polymers are breakdown into monomers by the help of hydrolysis process in which breakdown of bonds occur or lysis process of bonds occur by the addition of a water molecules. During this reaction, a molecule made up of many subunits is split in two: one of the new get hydrogen molecule and other is gaining hydroxide molecules by water. |
|
|
3.1 |
||
|
Mark:
10 |