INTRODUCTION
Cell biology is that branch of biology which deals with the structure, behaviour and function of the cells. All living organisms are made up of cells and they are responsible for facilitation of life. Cell biology involves the formation of cells, their division and the process of differentiation of cells. Cell anatomy, respiration and death are associated with the study of cell biology. This report highlights the structural and functional outcomes of eukaryotic cells along with the organisation of DNA and RNA in eukaryotic cells. The main discussion revolves around the events of cell cycle and how cleavage and gastrulation results in formation of the germ layer.
TASK 1
QUESTION 1.
Given below is a labelled diagram of eukaryotic cell of a plant:
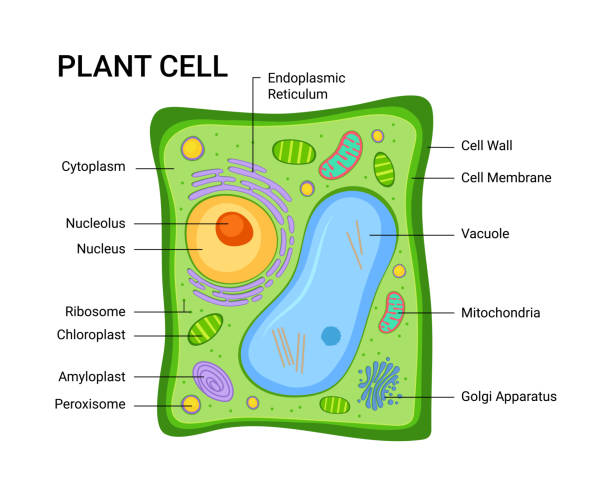 |
Illustration 1: eukaryotic plant cell
Source: https://www.istockphoto.com/illustrations/eukaryotic-cell
 |
Illustration 2: Eukaryotic animal cell
Source: https://www.britannica.com/science/eukaryote
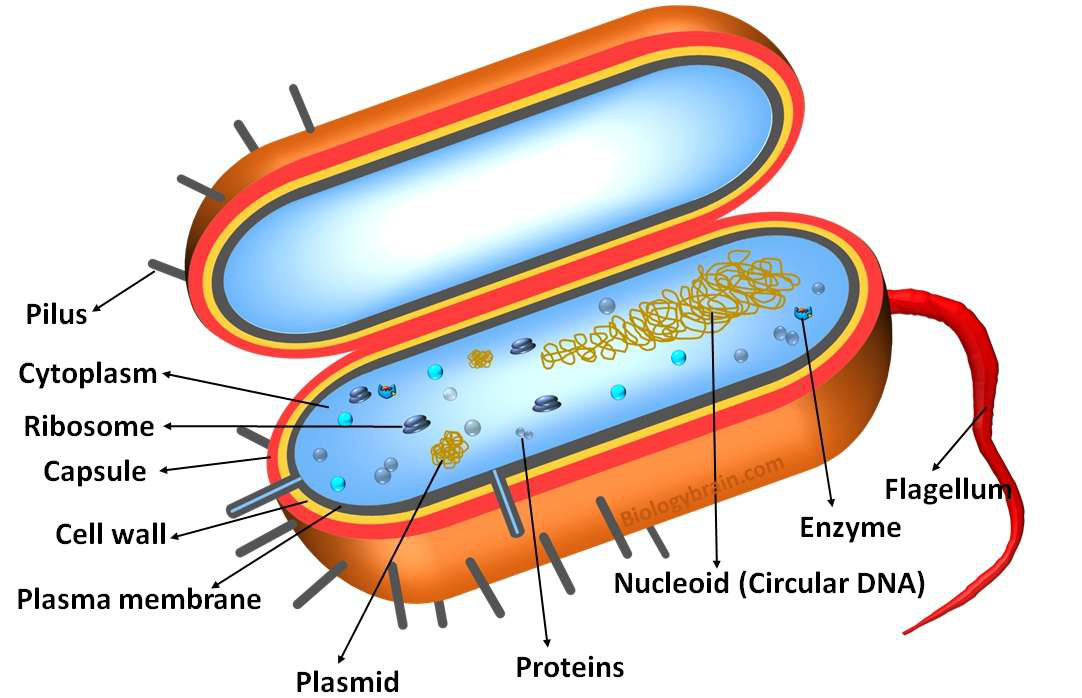 |
Illustration 3: Prokaryotic cell
Source: https://www.biologybrain.com/labeled-prokaryotic-cell-diagram/
QUESTION 2.
|
Organelle |
Functions |
|
Nucleus |
The main function of nucleus is the storage of DNA. The blueprint of the genome is essentially preserved in this organelle. |
|
Mitochondria |
It is also known as the powerhouse of the cell and is responsible for the production of energy. |
|
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum |
The main function of the SER is production of lipid and detoxification of the cell. |
|
Rough endoplasmic reticulum |
It facilitates the production of the protein and carries out the export and import of substances from the cell to the nucleus. |
|
Golgi apparatus |
The Golgi complex acts as a factory where proteins are received from the ER and further transported to the desired department (Keller, Davidson and Shook, 2003). |
|
Peroxisome |
Diverse oxidative reactions are sequestered in the peroxisome that play an important role in metabolic processes. |
|
Lysosome |
Acts as digestive system of the cell and helps in degrading and digesting the components of the cell within itself. |
|
Vacuole |
Mostly found in plants, helps in maintaining water balance and in animal cells helps in sequestering of waste products. |
|
Cytosol |
It is the liquid found inside of the cells where all the other organelles float. It is involved in the signal transduction between the nucleus and organelles. |
|
Centriole |
Organization of microtubules and acts as the skeletal system of the cell. Only present in the animals. |
|
Vesicle |
Facilitate the recycling of materials that are needed by the organism to survive. They prevent cell damage and save the cell from infection. |
|
Ribosome |
These are the sites of protein synthesis and translates the genetic code into string of amino acids for the formation of proteins. |
The organelles involved in protein synthesis starts when RNA polymerase converts the DNA of the gene into mRNA. This mRNA is carried to RER where the formation of proteins occur with the help of ribosomes and enzymes through the process of transcription. The chain of amino acids are packed altogether and transported to the Golgi apparatus for modification of the polypeptide chain into mature proteins which is followed by the release of the protein in the extracellular environment through plasma membrane (Kummer and Ban, 2021).
QUESTION 3.
Bulk transport is the movement of macromolecules in and out of the cell and there are two ways through which this happens- endocytosis and exocytosis. The mechanisms of both these processes are involved in the transport of substances in and out of the cell. These mechanisms are involved in the transportation of big molecules such as proteins, polysaccharides and hormones with the help of a vesicle. Both these processes require energy in the form of ATP for the conduction hence, both these processes examples of active transport. However, endocytosis transports materials inside the cell and exocytosis facilities the transport of the molecules out of the cell. Endocytosis takes up substances from the external environment whereas exocytosis is involved in the elimination of waste.
|
Function |
Endocytosis |
Exocytosis |
|
Mechanism |
There is formation of an endocytic vesicle around a substance or a macromolecule whether solid or liquid (Dopp, Tamiev and Reuel, 2019). |
Fusion of the vesicle containing the waste with the plasma membrane occurs in order for elimination to happen. |
|
Types |
Occurs through phagocytosis and pinocytosis |
Occurs through constitutive and secretory pathways |
|
Vesicles |
Internal vesicles are formed e.g., phagosomes |
Secretory vesicles are formed |
|
Examples |
Engulfing of bacteria |
Release of hormones |
TASK 2
QUESTION 1.
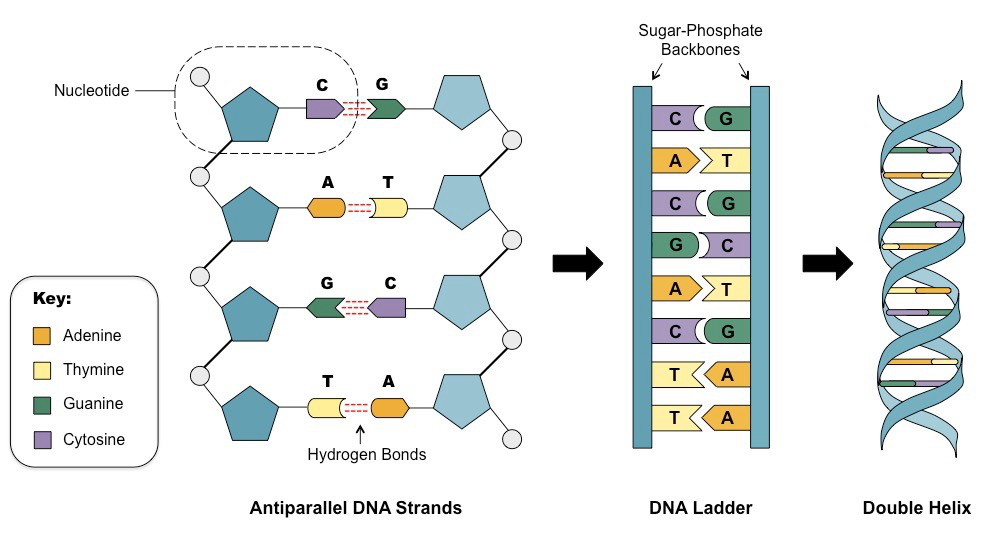 |
Illustration 4: Structure of the DNA
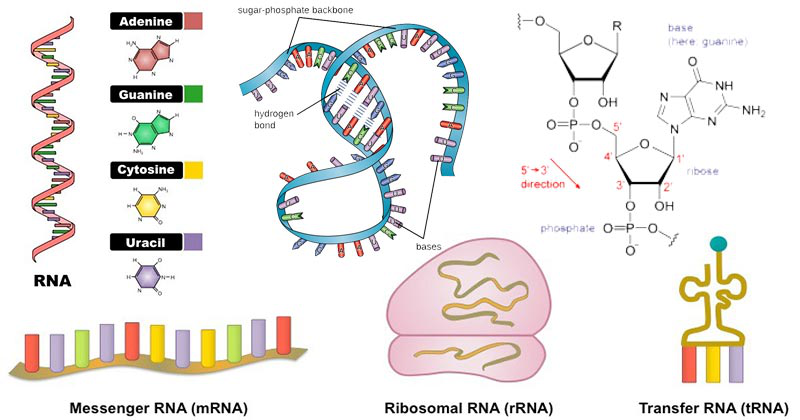 |
Illustration 5: Structures of different types of RNA
Source: https://microbenotes.com/rna-properties-structure-types-and-functions/
The information of the whole genome is stored inside the DNA which is located inside the nucleus of the cell. There are four chemical base pairs that consist of the structure of the DNA: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine (C) and thymine (T). These sequence of these bases determine the building up and maintenance of the organism for life. These base pairs attached to the sugar molecule and a phosphate group altogether from a nucleotide (Webster and Weixlbaumer, 2021). These nucleotides are arranged in a double helix spiral fashion. The DNA molecule is packed in the form of thread like structures that make up the chromosomes. A DNA is highly coiled many times around a protein named histone that support the structure of the chromosome. A chromosome is an X shaped structure that contains a constriction point called centromere. This centromere divides the chromosome into arms. The shorter arm is called Q arm and the longer arm is called P arm. The DNA is transcribed into RNA in eukaryotic cells and the newly produced RNA is transported into the cytoplasm where the RNA is converted into protein with the help of ribosomes. It is mostly found in the cytoplasm. However in prokaryotic cells, the RNA is present inside the nucleus. For effective expression of the gene, the transport of RNA from nucleus to the cytoplasm is fundamental (Schäfer and et. al., 2019).
QUESTION 2.
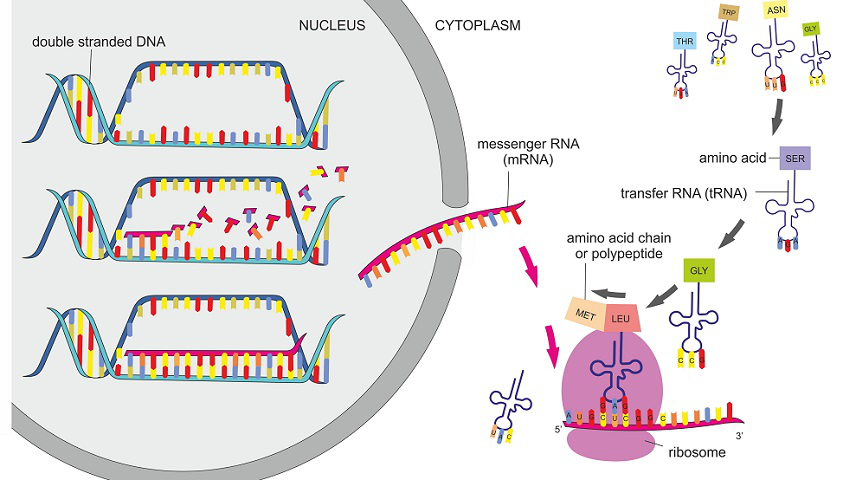 |
Illustration 6:Transcription
Source: https://biologydictionary.net/protein-synthesis/
Transcription is the process of copying a part of DNA into RNA. These segments of DNA are converted into RNA molecules that encode the amino acids which are necessary for production and maturation of proteins in the body. Transcription occurs in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells and cytoplasm in prokaryotes. The template DNA strand is used to reproduce mRNA or messenger RNA that is also made complementary to the strand of DNA used. These transcribed mRNA are translated into functional proteins. The process of transcription is divided into three steps: initiation, elongation and termination. Initiation marks the beginning of transcription. A segment of the DNA called gene is marked as promoter and RNA polymerase binds to the promoter which signals the DNA to uncoil in order to help the enzyme identify the bases in that promoter strand. Once identified, the enzyme is set to produce a complementary sequence of bases (Song, Li and Zeng, 2021). The process of elongation is characterized by addition of nucleotides to the mRNA which reds the DNA strand and produced mRNA with the use of base pairs with the help of RNA polymerase. The adenine is replaced with uracil during the production of RNA. The last step termination is the ending of transcription which occurs when the enzyme RNA polymerase reaches the stop codon in the sequence of the gene. Once the process is complete the mRNA detaches itself from the DNA. The process remains the same in prokaryotic cells however, the promoters in prokaryotes (such as bacteria) are composed of three sequence elements whereas in eukaryotes there are seven promoter elements.
TASK 3
QUESTION 1.
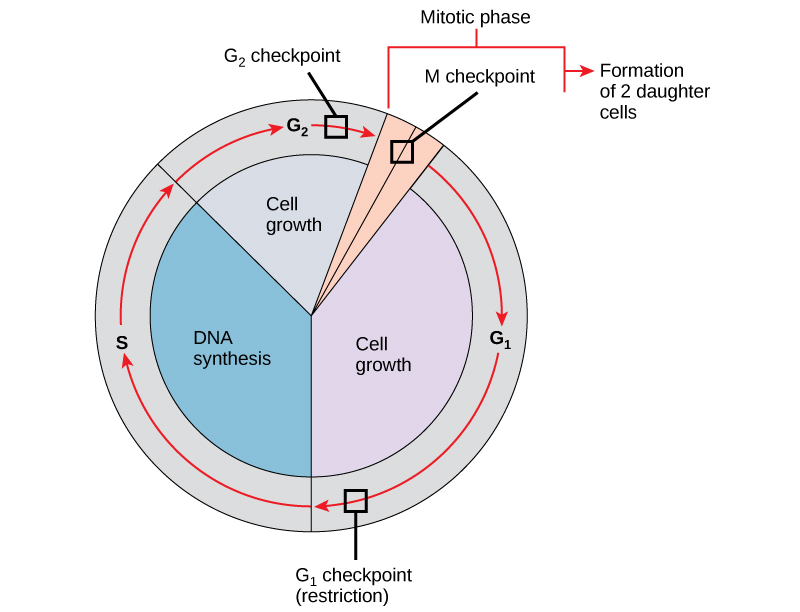 |
Illustration 7: Cell cycle
Source: https://courses.lumenlearning.com/suny-wmopen-biology1/chapter/cell-cycle-checkpoints/
There are four main phases in a cell cycle. The first three phases are referred to as interphase and the fourth phases is called mitosis.
- G1 phase- This phase is characterized by the growth of the cell where there is an increased production of mRNA, protein and all the organelles prepare for further stages of division.
- S phase- The production or replication of other organelles is halted and the synthesis of DNA is done. All the DNA is replicated and one copy of each chromosome is created. This replication of DNA is followed by formation of sister chromatids joined together at the centromere.
- G2 phase- The growth of the cell continues and the final replication is done (Godard and Heisenberg, 2019).
- M phase- This phase involves the breakdown of nuclear membrane where the sister chromatids are finally separated and the nuclei are pulled to the sides of the cell. This is followed by splitting of the cell membrane and the cytoplasm into equal parts. This leads to formation of two daughter cell that are identical.
- G0 Phase- After the completion of M phase, the cell can either enter the G1 phase again or enter G0 phase, which means that a cell is functional but cannot divide.
Major checkpoints of the cell cycle are G1, G2 and M checkpoint.
- G1 checkpoint- This restriction checkpoint takes place between G1 and S phase. The cell verifies that the size of the cell, the intact structure of the DNA and whether or not enough nutrients and stimulating factors are accessible to the cell.
- G2 checkpoint-This checkpoint confirms the quality of DNA if it correctly and completely replicated. It ensures that damaged DNA is not passed onto the daughter cells.
- M checkpoint- This checkpoint examines the attachment of sister chromatids to the spindle microtubules in all the chromosomes (Okuchi and et. al., 2021).
QUESTION 2.
|
Mitosis |
Meiosis |
|
|
Metaphase |
Individual chromosomes line up on cell's equator |
Pairs of chromosomes line up on cell's equator |
|
Prophase length |
Short prophase length |
Longer prophase I |
|
Anaphase |
Sister chromatids move to opposite ends of cells |
Sister chromatids move to the same pole of the cell during anaphase I whereas in anaphase II sister chromatids are separated. |
QUESTION 3.
Mitosis is the process by which there is replication and segregation of chromosomes for production of two identical nuclei which is followed by equal division of the contents of the cell into two daughter nuclei that consist of identical genomes. Mitosis is also called equational division. The total number of chromosomes are maintained during this process. The start of mitosis is characterized by the S phase of the interphase where there is replication of DNA. The components of the cell such as cytoplasm, organelles and cell membrane are equally divided in the telophase and cytokinesis. During mitosis, chromosomes are duplicated, condensed and attached to the spindle fibres that pull the copy of each chromosome to the opposite sides of the cell. Two identical daughter nuclei are produced which is followed by cytokinesis where the rest of the organelles of the cell divides producing two daughter cells (Jabbar and et. al., 2020). The main aim of mitosis is to ensure that the two daughter cells have an equal amount of component. Mitosis ensures the growth of the organism that have the same genetic component. The repair and replacement of the cells in the body is done through the process of mitosis.
TASK 4
QUESTION 1.
The amount and distribution of yolk protein in the cytoplasm affect the angle of the mitotic spindle and timings at which it is formed. It also determines where cleavage occurs and also the size of the blastomeres. The cellular division occurs at a faster rate when one pole of the egg is free of the yolk. The pole that is rich in yolk is called as vegetal pole and the concentration of the yolk in animal pole is very low. Yolk inhibits the formation of cleavage. Holoblastic or complete cleavage extends throughout the entire egg whereas meroblastic cleavage is when only a part of cytoplasm is cleaved. There is no penetration of cleavage furrow into the yolk of the cytoplasm. The pattern of the cleavage is highly determined by the quantities of the yolk within an egg.
Related Samples: Cell Biology and Biochemistry Workbook
QUESTION 2.
The gastrulation process in a sea star starts during the late blastula stage where a few cells that are developed in the embryo begin to turn into a blastocoel which consists of 8 cells. The process of gastrulation becomes distinct when the embryo is called gastrula (9 celled embryo). Indentation of gastrulation occurs when the gastrula turns into a blastopore which is basically 10 celled embryo.
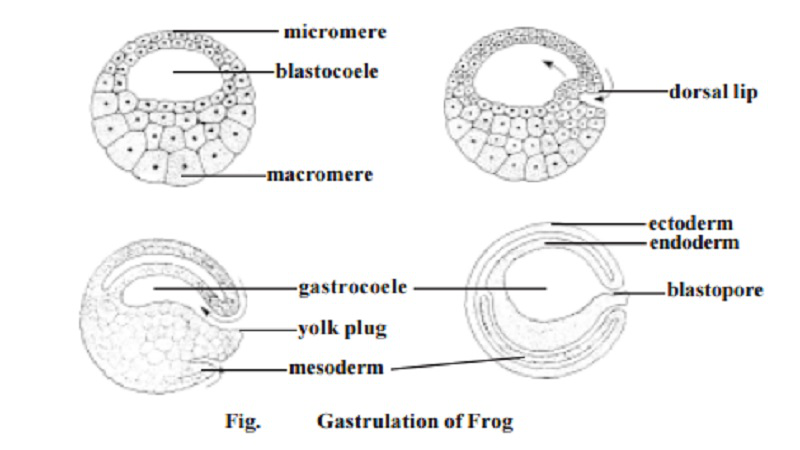 |
Illustration 8: Gastrulation process in a frog (amphibian)
Source: https://www.brainkart.com/article/Gastrulation-in-frog-embryo_671/
The blastodermal cells begin to move and wander around to form the organs in the amphibian along with occupying blastocoelic activity.
The gastrulation in chick embryo involves the formation of primitive streak which is already achieved on the second day of incubation. The blastula enables the formation of the germ layers and occurs after cleavage but before organogenesis (Miyauchi, Ohta, and Saitou, 2018).
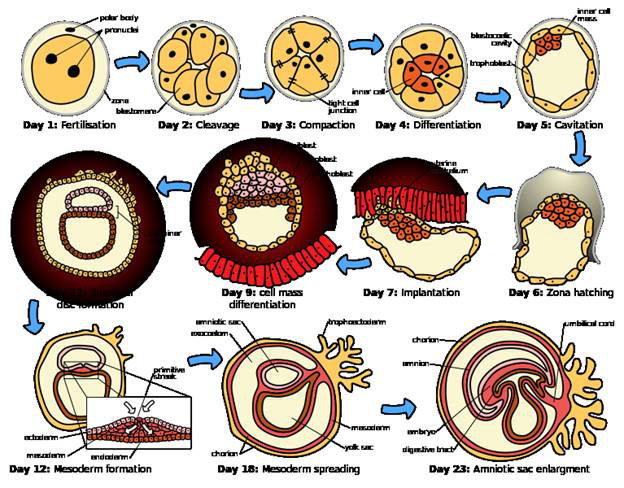 |
Illustration 9: Gastrulation in human embryo
Source: https://thebiologynotes.com/human-embryogenesis/
Gastrulation in humans occurs for 3 weeks and it is characterized by the generation of three germ layers- ectoderm, endoderm and mesoderm. The formation of these germ layers is extremely important for the generation of organs which is one of the most critical steps towards the development in humans.
QUESTION 3.
The similarities in a chick and a human embryo exists as chickens or thologs have 60% similarity of the human protein coding genes. The cellular fibro nectins of the human and the chick have been found to be almost similar. The presence of gill slits and tails have been observed in both the vertebrates. There is similar B cell development and NK cell biology. The dendritic cells and macrophages have been the same in both the organisms. The presence of eosinophils and basophils have been observed in both.
QUESTION 4.
Gastrulation is the process where the embryo transforms from one dimensional layer of epithelial cells into a multi dimensional structure. This process is critical for the development of the embryo and the differentiation of the cells. The three primordial germ layers are ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. When the blastula differentiates into specialized cells the stem cells in the embryo gives rise to the certain tissues that contribute to the embryonic development and even are first lineage specific. The cells that are differentiated into forming the inside of the organs derived from the endoderm. They line the gastrointestinal tract of the lungs, pancreas and other glands. However ectoderm forms the outer lining of the body which includes the skin and the hair. The cells that are derived from the mesoderm form the other tissues of the body such as the heart, muscles, dermis of the skin and also the bone marrow (Godard and Heisenberg, 2019). These germ layers arise from the stem cells and have the ability to give rise to a vast variety of organs and organ systems.
Related Samples: Cellular and Molecular Biology of Cancer
CONCLUSION
4 Cell Biology: Explore the intricate world of cells, their structure, function, and vital role in life processes. Case study help: From the above report, it can be concluded that eukaryotic cells have different levels of organizations defined by the presence and functions of different organelles. It was also concluded that a series of mitotic divisions, dividing large volumes of fertilized eggs into smaller ones, are called blastomeres, and the pattern of cleavage differs across species.
REFERENCES
Books and Journals:
Keller, R., Davidson, L.A. and Shook, D.R., 2003. How we are shaped: the biomechanics of gastrulation. Differentiation: ORIGINAL ARTICLE, 71(3), pp.171-205.
Kummer, E. and Ban, N., 2021. Mechanisms and regulation of protein synthesis in mitochondria. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 22(5), pp.307-325.
Dopp, J.L., Tamiev, D.D. and Reuel, N.F., 2019. Cell-free supplement mixtures: Elucidating the history and biochemical utility of additives used to support in vitro protein synthesis in E. coli extract. Biotechnology advances, 37(1), pp.246-258.
Webster, M.W. and Weixlbaumer, A., 2021. Macromolecular assemblies supporting transcription-translation coupling. Transcription, 12(4), pp.103-125.
Schäfer and et. al., 2019. Spx, the central regulator of the heat and oxidative stress response in B. subtilis, can repress transcription of translation‐related genes. Molecular Microbiology, 111(2), pp.514-533.
Song, B., Li, K. and Zeng, X., 2021. Monodirectional evolutional symport tissue P systems with promoters and cell division. IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed Systems, 33(2), pp.332-342.
Godard, B.G. and Heisenberg, C.P., 2019. Cell division and tissue mechanics. Current opinion in cell biology, 60, pp.114-120.
Okuchi and et. al., 2021. Wnt-modified materials mediate asymmetric stem cell division to direct human osteogenic tissue formation for bone repair. Nature Materials, 20(1), pp.108-118.
Jabbar and et. al., 2020. Prednisolone prophase for a week versus upfront multiagent chemotherapy in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia: An analysis with reference to induction mortality in a developing country. Journal of Pediatric Hematology/Oncology, 42(3), pp.181-184.
Miyauchi, H., Ohta, H. and Saitou, M., 2018. Induction of fetal primary oocytes and the meiotic prophase from mouse pluripotent stem cells. In Methods in Cell Biology (Vol. 144, pp. 409-429). Academic Press.
Online:


























