INTRODUCTION
Cells are the basic, fundamental unit of life which are the structural, functional and biological unit of all living beings. cell was discovered by the first biologist , Robert Hooke and it is the advancement of science. The structure and functions of cells help in better understanding the biological process of life in an appropriate manner (Choi and et. al., 2019). Cells provide support to the body of an organism and cells have different organelles surrounded by a separate membrane.This report includes the characteristics of living cells, differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and the role of the cell membrane in regulating nutrients. Lastly, it also includes cell growth and cell division.
MAIN BODY
SECTION-1
Cell structure
The cell is the basic structure and fundamental unit of life which performs a major function essential for the growth and development of an organism. The cell structure is composed of different components which include: cell wall, cell membrane, cell organelles, and cytoplasm (Tai, Tang, and Yan, 2019). The cell membrane is the outer covering of a cell that protects internal organelles from the environment. Cell theory is a scientific theory that describes living organisms as being made up of cells, which are the basic structure and function of all organisms (Thompson and Windsor, 2020). Cell theory was first proposed by German scientists Theodor Schwann and Matthias Jakob Schleiden in 1838, covering all plants and animals. The first nucleus was observed by Scottish botanist Robert Brown in 1833 (Yamamoto and Kitagawa, 2021). If you're finding it tough to grasp these concepts, you might consider seeking help to do my assignment and ensure understanding.
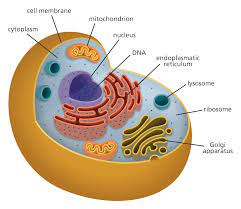
Figure:1 cell
Characteristics of living cells
Homeostasis- It is the internal environment which helps to maintain stable environment within itself and also changes outside the cell. Cell balance or control the stability of water inside the cell with respect to the quantity outside the cell. Cell also focus on detecting the changes in the concentrations of substances which is present inside the cell which includes sodium.
Growth and development- cell have certain growth and size because of intrinsic and extrinsic factors because it determines the cell growth and development at certain size. Growth factor of cell are rich in protein in the cell environment which is interconnected to the plasma membrane which controls cell to continuous growth (Schmidl and et. al., 2018). Growth factor is one of the essential factor which helps in promoting the wound healing of cell and protect cell from wounds. Cell grow at certain point and they have certain size during their life.
Internal and external cell movement- Movement in cell generates within both unicellular and multicellular organisms. Cell can also move independently and without the support of another cell. Cell can be move with the help of thin external structure such as cilia and flagella. The cell movement is inside the organelles inside the cell moving to other parts of cell. The internal movement of cell is supported with the help of internal cytoskeleton.
Cell reproduction- Cell is reproducing with the process of mitosis which is called as cell division. Cell divides into two parts which is unicellular and multicellular organisms. Mitosis is a fundamental process of life which may grow and regenerate. Cell reproduction is the process of cell division into two identical cells which is parent cell divides into two daughter cells. Cell division is the larger cell cycle which have different phases mitosis and meiosis (Lu and et. al., 2019).
Cell energy- Cells generate energy from the breakdown of food molecules. The cell requires constant energy to generate and maintain the function of the body. The mitochondrial process provides the energy from a molecule which is known as ATP (Adenosine triphosphate). Complex organic food molecules such as sugars, fats and proteins are rich sources of energy for cells that helps in providing cell nutrition and energy for biological process and maintain the function of cell.
Difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cell- It is the unicellular organism which is lack of membrane bound structure and prokaryotic cell is small in size and having simple cell structure, the prokaryotic cell size is approx. 0.1-5μm diameter (Balan, Saxena and Bhardwaj, 2019). Prokaryotic cell can divide the cell into two domains which is bacteria and archaea. Prokaryotic cell do not have mitochondria and a nucleus. That DNA in prokaryotic cell is found in circular form of DNA with single chromosome, this cell organism is lack of membrane bound structure. In prokaryotes cell having nucleoid region without the membrane bound nucleus (Nakamura and et. al., 2019).
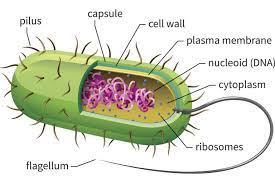
Figure:2 Prokaryotic cell
Eukaryotic cell- Eukaryotic is the larger cell as compared to prokaryotic cell, it protects and supports the plasma membrane. The cell is covered by the plasma membrane which helps in controlling the exit and entry of different substances. Eukaryotic cells either be unicellular or multicellular which have a true nucleus along with membrane bound organelles (Igarashi and Kashiwagi, 2019). Eukaryotic possess a cell wall and it also contains nucleus which have DNA.
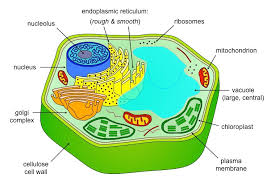
Figure:3 Eukaryotic cell
Impact of viruses on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
virus uses both cells, either prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells as a host cell which may also changes the cellular transcriptional activity and protein - protein interaction.Most of the viruses suppress the synthesis of host cells such as DNA, RNA, macro-molecules and proteins. In eukaryotic cells, the virus has receptors for the cells that attack and then enters and replicates the genetic material in the nucleus (Bitler, Dover and Shai, 2018). On prokaryotic cells virus induced mortality of micro-organism which can eliminate the production of prokaryotic cells. Virus can also transfer carbon and nutrients in prokaryotic cells at high level.
Compare and contrast of Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic cell
|
Types of cell characteristics |
Prokaryotic cell |
Eukaryotic cell |
|
Cell wall |
||
|
Cell size |
The size from 0.2- 2.0 in diameter. |
The size range from 10- 100 in diameter. |
|
Nucleus |
Having nucleoid in cell and nucleus is absent. |
Present |
|
Mitochondria |
Absent |
Present |
|
Cytoplasm |
Cell organelles absent but cytoplasm present |
Present with cell organelles. |
|
Plasmids |
Present |
Found very rarely in eukaryotic cells |
|
Ribosome |
Smaller in size |
Larger in size |
|
Cell division |
With the help of binary fission |
With the help of the mitosis process |
|
Cell reproduction |
Asexual |
Both asexual and sexual |
|
Ribosome |
Smaller in size |
Larger in size |
|
Lysosome |
Absent |
Present |
Discussion over Eukaryotic subcellular structure and organelles
Eukarytoic cells are found in animals,plants, algae and fungi and the fundamental component of cell are the organelles (Chavez and et. al., 2021). The cell organelles are composed of different combinations and have different functions of the cell, from metabolism, replication and energy production. There are various organelles with different functions, which include-
Plasma membrane- It is a phospholipid bilayer which is attached with proteins that separates the cell from its surrounding. The main function of the plasma membrane is to control the exit and entry of organic molecules such as water,oxygen, ions and other substances into and out of the cell.
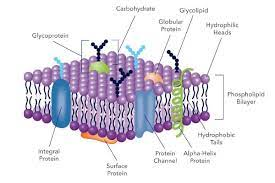
Figure:4 Plasma membrane
Cytoplasm- Cytoplasm is located in the cell between the plasma membrane and the nuclear envelope .It is composed of 70-80% water but it has no consistency like a semi-solid cytoplasm, contains other organic substances which include protein, sugar , fatty acids, amino acids, ions and water soluble molecules.
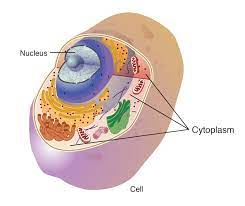
Figure:5 cytoplasm
Nucleus- It is one of the most outstanding organelles in the cell which stores chromatin in a gel like structure neoplasm. Nucleus is covered with a nuclear envelope and contains genetic information. Plants and animals contain eukaryotic cells with different functions (Tian, Zhan and Lin, 2022).
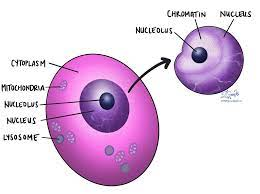
Figure:6 Nucleus
Mitochondria- This cell organelles is called the powerhouse and energy factory of the cell because it is the site of respiration in eukaryotic cell. It is the production of ATP energy which gives energy to the cell for biological processes. Mitochondria possess genomes which encode the functions of the cell.
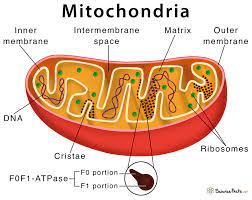
Figure:7 Mitochondria
Ribosomes- It is the cellular structure which has function of protein synthesis and it is located in the cytoplasm in the cluster like structure. Ribosomes are the large complex of protein and RNA and it is responsible for the translation process.
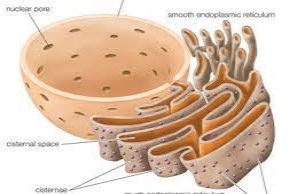
Figure:8 Ribosomes
Endoplasmic Reticulum: It is the large dynamic structure which has a main role in calcium storage, protein synthesis and lipid metabolism. The largest organelles of eukaryotic cells which is enclosed by a cell membrane which extends the nuclear membrane through cytoplasm (Obara, Moore and Lippincott-Schwartz, 2022).
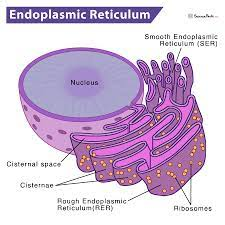
Figure:9 Endoplasmic reticulum
Cell wall- Cell wall is the structured layer which is surrounded by a plasma membrane of a plant cell which provides protection for cell against osmotic pressure. It is the network of cellulose and mircofibrilis.
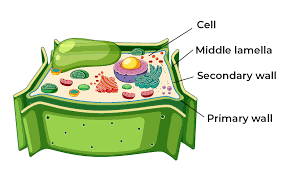
Figure:10 Cell wall
Lysosome- It is the membrane enclosed organelles which are found in animal cells. Lysosome contains hydrolytic enzymes which helps in breakdown the cell component such as carbohydrate, proteins and lipids.
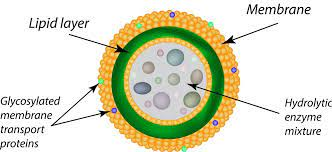
Figure:11 Lysosomes
Chloroplast- Chloroplast are the plant cell organelles which have the main function of converting light energy into chemical energy with the help of the photosynthesis process.
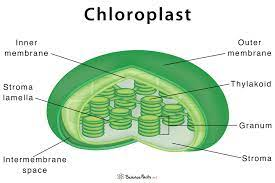
Figure:12 chloroplast
SECTION-2
Cell metabolism – It is symbolising as network of biochemical reactions occur in living organism in order to maintain life. It involves sequence of metabolic pathways. The mitochondria are main powerhouse of the cell where bioenergetics process are being occur.
Role of cell membrane in regulating nutrients.
Cell is symbolising are basic functional unity of body Every cell in body is enclosed by the cell membrane which includes plasma and internal membrane. These membranes composed of phospholipids, cholesterol, proteins and carbohydrates. Cell membrane act as barrier which help cell to separate from the external environment in optimise manner. There are two main functions of the cell membrane, firstly, to allow the transport of essential nutrients in and out of the cell. Specific transmembrane proteins carry out the diffusion of smaller charged molecules. However, the transport of larger molecules is not facilitated through smaller pores on phospholipid membrane (Parra, Stahl and Hellmann, 2018).
How animal cells use nutrients for growth and cell division.
Energy is being delivered to the body through the food consumed by the individual. Food is main source of energy which is essential to perform cellular activities in body. Energy in body came from three main nutrients carbohydrates, fats and protein. At cellular level food are being metabolised in order to make ATP. They are metabolised through cellular respiration where oxygen is being required and is called aerobic respiration. Four stages through which ATP is being produced are glycolysis, the link reaction, Kreb Cycle and electron transport cycle.
Glycolysis - It is the process in which glucose molecule is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate and process taken place in cytoplasm of cell. The end product of the reaction is 2 pyruvates, 2 ATP and 2 NADH molecule. They are primary step of cellular respiration. Glycolysis pathway occur in following stages:
- Stage 1- Phosphate group is being added to glucose in cytoplasm of cell which done through hexokinase enzyme. End of this stage, phosphate group is converted from ATP to glucose to form glucose, 6-phosphate.
- Stage-2 Further with help of enzyme phosphoglucomate, Glucose-6-phosphate is ismoerised into Fructose, 6-phosphate.
- Stage-3 Phosphate group is added from the ATP where the fructose, 6-phosphate is coveted into fructose 1,6-biphosphate. The action is being performed through enzyme phosphofructokinase.
- Stage-4 With help of aldolase fructose 1,6-biphosphate is converted into isomers. They are glyceraldehyde 3-phasphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate.
- Stage-5 Enzyme triose-phosphate isomerase converts dihydroxyacetone phosphate into glyceraldehyde 3-phasphate (Chandel, 2021).
- Stage-6 Simultaneously 2 reactions are being performed in this stage. With help of glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate to form NADH + H+.Enzyme assist in transferring 1 hydrogen molecule from glyceraldehyde phosphate to nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide. Enzyme also add phosphate to oxidised glyceraldehyde phosphate to form 1,3-biphosphoglcerate.
- Step-7 Through enzyme phosphoglycerokinase, phosphate is transferred from 1,3-bisphosphoglycerate to ADP in order to form ATP. Phosphoglycerate enzyme are being absorbed by end of reaction and ATP molecule.
- Step-8 By enzyme phosphor glyceromutase 2-phosphoglycerate is big formed.
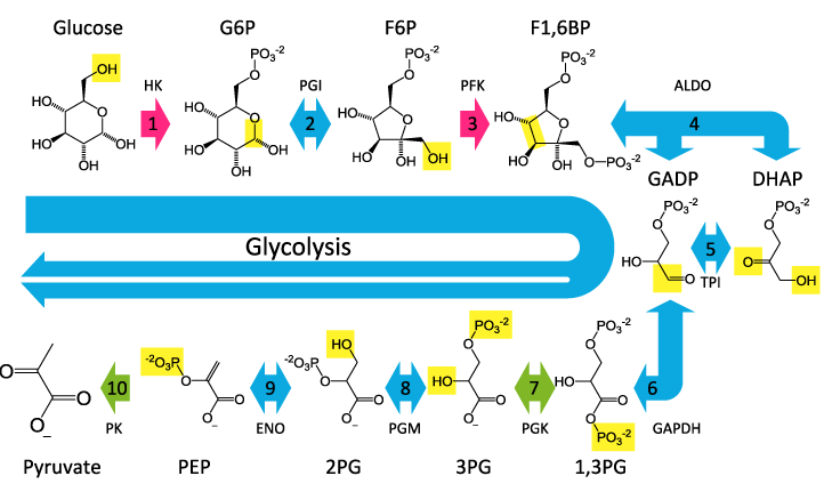
(Figure 11; Glycolysis pathway)
- Step-9 Enolase enzyme is responsible from removing water molecule from 2-phosphoglycerate to form phosphenol pyruvate.
- Step-10 By the action of pyruvate kinase a phosphate from phophenol pyruvate is transferred to ADP from pyruvate and ATP.
Link reaction – The end product of glycolysis enters mitochondria through transport protein. It is process where a carbon atom is removed from Pyruvate with aim to form carbon dioxide. In this process, Pyruvate combine with coenzyme A to produce acetyl-CoA.
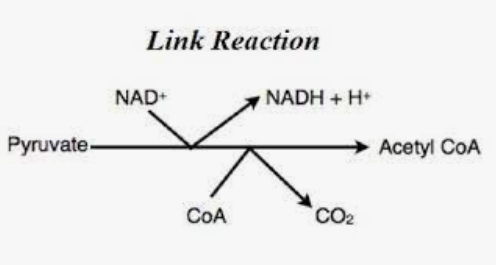
(Figure 12: Link Reaction)
Kreb Cycle – It is a process which takes place in mitochondria. In this process Acetyl-CoA combine with Oxaloacetate to form citrate. The form product is used to produce energy rich activated carrier molecule. After completion of every cycle 2 molecules of carbon dioxide are produced, 3 molecules of NADH and one molecule of GTP and one molecule of FaDH2 (Alderson and et. al., 2022).
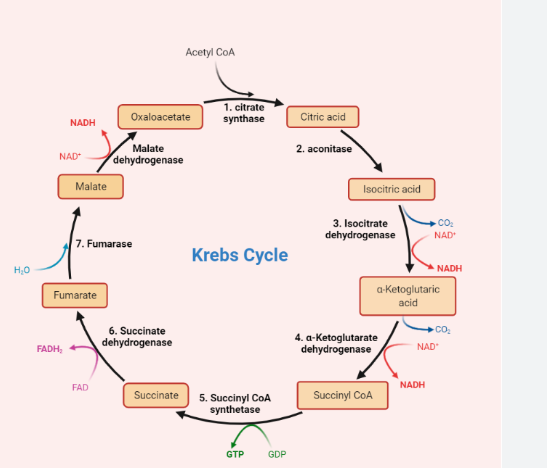
(Figure 13: Kreb cycle)
Cellular metabolism through synthesis of proteins
Protein synthesis is the process through which cell make protein. The main stage through which synthesis occur is transcription and translation. In eukaryotic cells, transcriptions take place in nucleus. Here DNA is converted into RNA. Mature mRNA is converted through splicing, editing, 5 Capping and polyadenylation. The ribosome reads the sequence of codons in mRNA and tRNA in accurate sequence. Translation occurs in three stages which are initiation, elongation and termination. At end of process, polypeptide chain is being synthesized where additional actions are being process in order to form completed protein.
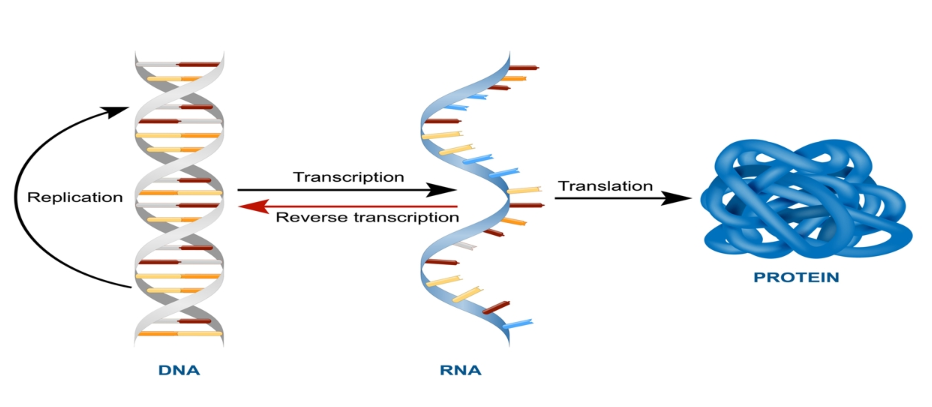
(Figure 14: Protein synthesis)
SECTION-3
Process through embryo stem cells generate
Stem cells are symbolise as the unspecialised cell which can easily develop into other type of cell. They are the cell which are found in embryo which further convert into specialised cell in order to develop the foetus. The division in stem cell occurs through mitosis. Sperm fertilize egg and form single cell namely zygote. Zygote form a cluster after division known as blastocyst. Blastocyst has outer layer known as trophoblast which help in protecting placenta. As embryo goes pluripotent cell develop into multipoint stem cells. (Padgett and Santos, 2020).
Importance of Interphase
Cell division is symbolise as the process through which parent cell divided into two daughter cells. It is the process by which new cells are being formed for growth, replacement and repairing in the body. Interphase is longest part of the cell cycle. It is phase when cell grows and copies its DNA before transferring into mitosis. S phase is characterised as the most important phase where the genetic material are being copied (Matthews, Bertoli and de Bruin, 2022).
- G1 phase: It is called as first gap phase where cell grows physically longer. Moreover the organelles expand, where the cells are metabolically active without incorporating DNA replication.
- S phase: Here, cell synthesize a complete copy of DNA in the nucleus. In this phase centrosome are also duplicate which help DNA separation during Mphase.
- G2 phase: It is symbolise as the second gap phase where cell grows more. Here cells form protein and organelles. The G2 phase ends when mitosis begins.
Factors that initiate cell division
Cell organelle is responsible for initiating cell division in centriole. It assists while producing the mitotic spindle fibres which act as the crucial part in the process of cell division in organism. Other than cell organelle, cell division can be initiated through growth-promoting hormone HGH. The centriole located in cytoplasm is involved in cytokinesis where cytoplasm begins to divide (Wong and et. al., 2021).
Related Samples: Biology Misconception
Importance of mitosis in cell
Mitosis is used to produce daughter cells which are genetically identical to produce parent cell. It is the process of nuclear division in eukaryotic cell which is divided into five stages namely prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, telophase and anaphase.
- During prophase replicated pairs of chromosome converted into chromatids and become visible. Nuclear envelope breakdown and centrosomes move towards opposite pole.
- In prometaphase chromosome continue condense where mitotic spindle microtubules attach to kinetochores (Petsalaki and Zachos, 2020).
- During metaphase, microtubule pull sister chromatids back and forth until alignment done in plane.
- In anaphase, sister chromatid are separated simultaneously at centromeres which are further pulled by the spindle of opposite poles of cell.
- In telophase, nuclear membrane is being formed in prominent manner around each set of chromosome. Cytokines is being undergone in process that divides the cytoplasm of parental cell into daughter cell (Godard and Heisenberg, 2019).
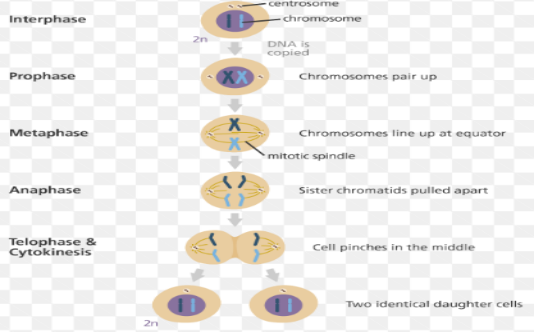
(Figure 16: Mitosis stages)
Compare cancer cell with normal cell- The nucleus of a cancer cell is larger in size and darker than that of an normal cell. Normal cells have normal DNA and have normal number of chromosomes while cancer cells often have an abnormal number of chromosome and cancer cells does not stop growing and they grow rapidly and divide before cells are fully mature (Rottenberg, Disler and Perego, 2021). The major difference between normal cells and cancer cells is that normal cells perform function while cancer cells may not be functional. Normal cells get energy in the from of molecule ATP and many cancer cells produce their energy through glycolysis process (Klaunig, 2018).
|
CANCER CELL |
NORMAL CELL |
|
They posses small cytoplasmic nuclei when compared with normal cell. They are even large and posses variable nuclei. |
They are small, uniformly shaped nuclei which posses relatively the larger cytoplasmic nuclei. |
|
Glycolysis lead ot lactic acidosis. |
Aerobic glycolysis takes place. |
|
Unregularly angionesis |
Control angiogensis. |
|
Larger number of dividing cells present. |
Lower magnitude of dividing cells. |
|
Disorganised cell arrangement is being seen (Devin and et. al., 2019). |
Here cell are being arranged into discrete units. |
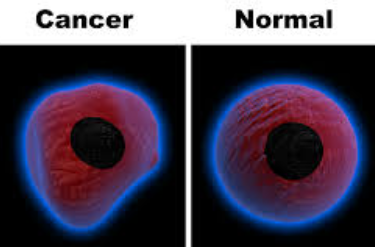
(Figure 17: Cancer cell vs normal cell)
CONCLUSION
From the above discussion, it is concluded that the cell is the structural and functional fundamental unit of life, helping in controlling and maintaining biological processes. The cell provides energy and nutrients to the body and protects it from bacterial infections or viruses. Cells have various components that protect them and maintain the concentration of water and other substances inside the cell. Cell division occurs through mitosis and meiosis, producing two identical copies of the daughter cell. Using a dissertation outline generator can assist in organizing research related to these cellular processes effectively.
REFERENCES
Books and Journals:
Alderson, N.L., Wang, Y., Blatnik, M., Frizzell, N., Walla, M.D., Lyons, T.J., Alt, N., Carson, J.A., Nagai, R., Thorpe, S.R. and Baynes, J.W., 2022. S-(2-Succinyl) cysteine: a novel chemical modification of tissue proteins by a Krebs cycle intermediate. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics, 450(1), pp.1-8.
Balan, S., Saxena, M. and Bhardwaj, N., 2019. Dendritic cell subsets and locations. International review of cell and molecular biology, 348, pp.1-68.
Bitler, A., Dover, R.S. and Shai, Y., 2018, January. Fractal properties of cell surface structures: A view from AFM. In Seminars in Cell & Developmental Biology (Vol. 73, pp. 64-70). Academic Press.
Chandel, N.S., 2021. Glycolysis. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, 13(5), p.a040535.
Chavez, J.D., Wippel, H.H., Tang, X., Keller, A. and Bruce, J.E., 2021. In-cell labeling and mass spectrometry for systems-level structural biology. Chemical Reviews, 122(8), pp.7647-7689.
Choi, Y.J., Jun, Y.J., Kim, D.Y., Yi, H.G., Chae, S.H., Kang, J., Lee, J., Gao, G., Kong, J.S., Jang, J. and Chung, W.K., 2019. A 3D cell printed muscle construct with tissue-derived bioink for the treatment of volumetric muscle loss. Biomaterials, 206, pp.160-169.
Devin, J.L., Hill, M.M., Mourtzakis, M., Quadrilatero, J., Jenkins, D.G. and Skinner, T.L., 2019. Acute high intensity interval exercise reduces colon cancer cell growth. The Journal of physiology, 597(8), pp.2177-2184.
Godard, B.G. and Heisenberg, C.P., 2019. Cell division and tissue mechanics. Current opinion in cell biology, 60, pp.114-120.
Igarashi, K. and Kashiwagi, K., 2019. The functional role of polyamines in eukaryotic cells. Theinternational journal of biochemistry & cell biology, 107, pp.104-115.
Klaunig, J.E., 2018. Oxidative stress and cancer. Current pharmaceutical design, 24(40), pp.4771-4778.
Lu, Y., Xu, L., Cong, Y., Song, G., Han, J., Wang, G., Zhang, P. and Chen, K., 2019. Structural characteristics and anticancer/antioxidant activities of a novel polysaccharide from Trichoderma kanganensis. Carbohydrate polymers, 205, pp.63-71.
Matthews, H.K., Bertoli, C. and de Bruin, R.A., 2022. Cell cycle control in cancer. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 23(1), pp.74-88.
Nakamura, M., Yamaguchi, K., Kimoto, Y., Yasaki, Y., Kato, T. and Sugimoto, H., 2019. Cd-free Cu (In, Ga)(Se, S) 2 thin-film solar cell with record efficiency of 23.35%. IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 9(6), pp.1863-1867.
Obara, C.J., Moore, A.S. and Lippincott-Schwartz, J., 2022. Structural diversity within the endoplasmic reticulum—from the microscale to the nanoscale. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Biology, p.a041259.
Padgett, J. and Santos, S.D., 2020. From clocks to dominoes: lessons on cell cycle remodelling from embryonic stem cells. FEBS letters, 594(13), pp.2031-2045.
Parra, M., Stahl, S. and Hellmann, H., 2018. Vitamin B6 and its role in cell metabolism and physiology. Cells, 7(7), p.84.
Petsalaki, E. and Zachos, G., 2020. DNA damage response proteins regulating mitotic cell division: double agents preserving genome stability. The FEBS journal, 287(9), pp.1700-1721.
Rottenberg, S., Disler, C. and Perego, P., 2021. The rediscovery of platinum-based cancer therapy. Nature Reviews Cancer, 21(1), pp.37-50.
Schmidl, C., Delacher, M., Huehn, J. and Feuerer, M., 2018. Epigenetic mechanisms regulating T-cell responses. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, 142(3), pp.728-743.
Tai, Q., Tang, K.C. and Yan, F., 2019. Recent progress of inorganic perovskite solar cells. Energy & Environmental Science, 12(8), pp.2375-2405.
Thompson, A.G. and Windsor, C.R., 2020. Theory and strategy for monitoring the performance of rock reinforcement. In Geotechnical Instrumentation and Monitoring in Open Pit and Underground Mining (pp. 473-482). CRC Press.
Tian, M., Zhan, J. and Lin, W., 2022. Single fluorescent probes enabling simultaneous visualization of duple organelles: Design principles, mechanisms, and applications. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 451, p.214266
Wong, M.M.K., Joyson, S.M., Hermeking, H. and Chiu, S.K., 2021. Transcription factor AP4 mediates cell fate decisions: To divide, age, or die. Cancers, 13(4), p.676.
Yamamoto, S. and Kitagawa, D., 2021. Emerging insights into symmetry breaking in centriole duplication: updated view on centriole duplication theory. Current Opinion in Structural Biology, 66, pp.8-14.



















