Question :
This assessment will demonstrate:
- What are the effective roles of agencies in all the health in communities?
- What are the relationship in prevalence for disease for social care services?
Answer :
INTRODUCTION
Public health can be defined as the discipline along with an art of preventing diseases while extending the life and sponsoring the health and safety. For this, there are various healthcare organisations such as WHO, Public Health England which are operating at operated at national and local level. Health and well being of any community are major concern due to which such health organisations are responsible to manage, monitor and control the infectious as well as non-infectious diseases. The present assignment report is based on the case study on people of UK suffering from various diseases such as Sexually transmitted (STI) and HIV. The report includes different approaches and strategies used to measure, monitor and control the incidence diseases in communities. The present report also discusses the implications of illness and disease in communities for the provision of health and social care services.
TASK 1
1.1: Roles of Agencies in Identifying Levels of Health and Diseases in Communities
Public health is primarily concerned with organising measures either through private or public in order to prevent diseases, promoting health as well as prolong life among the varied population. For this, there are different agencies which are liable to identify the diseases and health in communities such as World Health Organisation, Health protection agency and Primary Care Trust. Each such agencies play a different but important role in determining health and disease levels and promotes healthier environment (Basile and Smith, 2011).
Local level: Health and Well-being board and CCG is a health agency operated at local level providing various care provisions to particular areas for example, if Wandsworth area is allotted to them then they are liable to eliminate the diseases of people such as STI and HIV living in that area only. Thus, they are responsible to provide health care services and determining the status of community during outbreaks.
National Level: Public Health England (PHE) is health organisation operated at national level also contributing maximum efforts in determining the levels of health and diseases. According to HPA act, the role of such institution is to protect the community from infectious diseases such as STI and HIV. This indicates that HPA is mainly focuses on minimising the harmful incidences and control breakouts through bringing some changes in the health level in a particular community (Brownson and et. al., 2017).
International Level: World Health Organisation is an organisation operated at global level contributing maximum in managing the health related issues such as prevention of STI/HIV diseases that are arises among young adults. It performs six core functions in order to prevent health related issues in community. Such functions includes:
- Engaging in partnership with other health care institutions so that they can serve maximum number of people live in rural as well as urban areas.
- Setting norms and standard and monitoring their implementation so that other health care agencies such as HPA are serving better health care services to people through complying such norms.
- Providing technical support to enhance the capacity of low operating health institutions so as to to reach their health related services to maximum number of people.
Relationships between Public Health England (PHE) and World Health Organisation
Both such organisation are working for enhancing the healthy lifestyle of people through awaking about the causes and consequences of infectious as well as non-infectious disease. It brings awareness in the society to consume healthy to live healthy through conducting several programs and campaigns. PHE is providing its services at local level whereas WHO are operating its services at global level but have same objective or goals. Therefore both such organisation are working to achieve common goals and objectives i.e. maintaining healthy lifestyle of people and community as a whole.
1.2: Epidemiology of One Infectious and One non-Infectious Disease
Gender: the state of being male or female (typically used with reference to social and cultural differences rather than biological ones)
Ethnic group: A community or population made up of people who share a common cultural background or descent
The infectious disease which is common in UK is Sexual Transmission diseases (STI) that are commonly spread by sexual activity especially vaginal intercourse, anal sex and oral sex. It has been observed that in UK consumption of alcohol is increasing due to which the people are going through with the issues of STI/HIV. In the year 2016, more than 417,584 new STI diagnosis were found in UK out of which 202,546 were suffering from chlamydia, 62,721 were suffered from genital warts, 36,244 were suffering from gonorrhoea and other 36,774 were suffering from non-specific genital infections. As compared with 2015, the new STIs diagnosed has been increased by 4% in 2016. The high population rates of STIs diagnosis are among people of black ethnicity (Rates of selected sexually transmitted infection (STI) diagnoses* by ethnicity and STI, 2016, England, 2018). It is clearly shown under the mentioned graph:
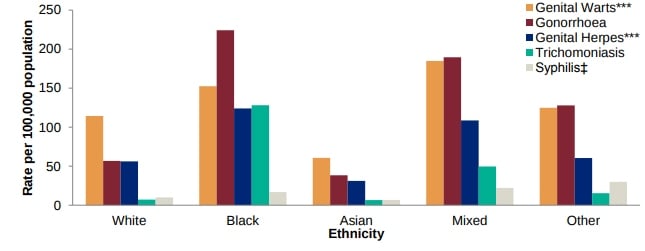
It has been also found that the people in age of 15 to 24 years are experiencing the highest STI diagnosis rates which is given on below graph. Compared to people aged 25 to 59 years, rates of STI diagnoses in this age-group are twice as high in men and seven times as high in women; these higher rates are likely due to greater rates of partner change among the younger age-group. The differences in group gender in terms of suffering HIV/STI, the main reason is alcohol which is mostly consumed by women in UK in their adult days due to which it gives rise to blood pressure which is a significant risk factor. Globally, 85% of HIV transmission is through heterosexual intercourse. Worldwide, almost half of people with HIV are women, whereas in the United States, male-to-male sexual contact still accounts for more than 60% of new diagnoses (How Is HIV Transmitted, 2018).
From the above graph, it has been seen clearly that Population in England from 2005 to 2017, the cases of STI are increasing on continuous basis in both male and female.
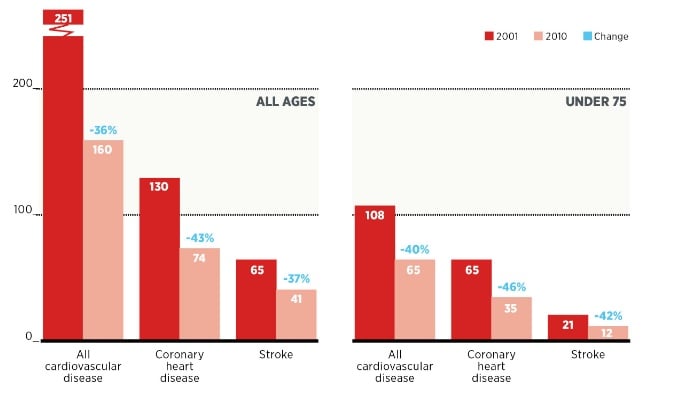
A non-infectious disease which is widely spread in the UK is cardiovascular diseases which are due to high level of alcohol consumption by children and adults (Alcohol consumption and cardiovascular disease, 2017). It is important to notice that the main reason behinds arising such disease is alcohol consumption as it gives rise to blood pressure which is a significant risk factor. Th graph mentioned below clearly shows that total 68% of the people are suffering from cardiovascular disease (UK Mortality from Cardiovascular diseases, 2018). NHS Health Check, which was supposed to provide 15 million adults between the ages of 40 and 74 with a cardiovascular examination by their GP. But by 2013 it had reached only a fifth of its target population; less than 5 per cent of patients were identified as high risk and of these only a third were getting the right treatment, according to a study commissioned by the Department of Health.
1.3: Effectiveness of the Implemented Processes
STIs disease cannot be controlled by clinical interventions alone as it is important to prevent such disease at the clinic and outside where the transmissions takes place. Such interventions mainly focuses on means of prevention, informations and referrals to clinical



















