Introduction
The storage and information processing for an organization in form of a computer based database is regarded as a Management Information System. The operations which are performed by each and every level of an organization are organized and programmed into the form of a daily report (Scherer and Schapke, 2011). Furthermore, the possibility of formulating special reports is also possible. With such a system, the managers are able to obtain feedback about their own performance. This accounts to be the main purpose served by MIS.
Through the use of Computer-Based Information Systems (CBIS), top-level management is able to do monitoring of processes. This allows comparison of information related to the past, present and future of an organization. It involves the usage of software helping towards decision-making processes. CBIS comprises database, hardware resources, decision support system, people and project management applications, along with additional computerized procedures for enabling the various departments within an organization to run efficiently and effectively.
There are different types of functions that are carried out in the computer-based information system. These include collection, processing, storing, analysis and distribution of data with a agenda or motive for accomplishing the business objectives. Information systems are a major component of this entire environment. Business processes are easily executed when these types of working systems are implemented and aligned with company objectives.
Differentiation between structured, semi-structured and unstructured decisions
Structured decisions
Within this category, all three main procedures of data, process, and evaluation are included. This comprises of routine based decisions that are taken on a regular basis. As contextualized by Tipton and Nozaki, (2012), whenever the management of an organization has to come across a problem then, they are able to get a more clear cut & effective solution with the help of structured decisions. These decisions are very much focused on finding the key solution to a problem. In order to take structured decisions, the Management Information System emerges out to be an effective tool. It can be analyzed that the methodology involved in determining and finding a particular solution towards a problematic situation in case of structured decisions is very well formulated and further executed. They are generally taken by a firm's lower management and staff on a daily regular basis. This category of decision is very well straight forwarded.
Semi-structured decisions
According to the statement given by Laudon, Laudon, and Brabston, (2011), this category of decision comes under the influence of somewhere in the middle of structured & unstructured decisions. While carrying the procedure of making decisions, this category requires the involvement of some sort of judgments from other people. In addition to this, agreements are also being made with respect to the final solution towards the problems within an organization. Semi-structured decisions are generally used by the middle management level.
Unstructured Decisions
The decisions coming under this category account to be very occasional along with the uniqueness in their nature. No such predefined procedure is there for solving these problems, which leads to a conclusion that, for every occurring problem, a new analyzation procedure has to be followed. The higher levels of management often address situations where unstructured decisions have to be taken(Unit 127 - Spatial Decision Support Systems, 2010). These also involve a high level of complexity within them. So, keeping this in mind, no already tried or true methods are available in order to handle them. Furthermore, they involve a much high-risk factor within them.
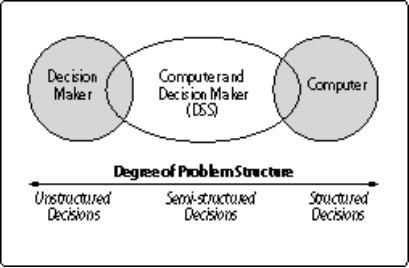
Figure 1 : Different types of decisions
(Source: Unit 127 - Spatial Decision Support Systems, 2010)
|
Strategic Level |
Tactical Level |
Operational Level |
|
The strategic level is the highest level of management in an organization. This level directly contributes to the achievement of the goals and objectives of an enterprise. |
The middle-level management is considered as tactical level because they have to deploy strategies for implementing the decisions. |
Ground-level management is considered as the operational level. |
|
Uncertain and dynamic decisions of the organization are to be taken at this higher level of management. |
The decisions regarding structured workflow, the foundation of distribution channels, etc. are taken at this level. |
The judgments regarding everyday operations and daily business activities are made at the operational level. |
|
Unstructured decisions are taken at this level of organization. |
Semi-Structured decisions are taken at this level. |
Structured decisions are taken by the operational management level. |
Strategic Level Tactical Level Operational Level
The strategic level is the highest level of management in an organization. This level directly contributes to the achievement of the goals and objectives of an enterprise.
The middle-level management is considered as tactical level because they have to deploy strategies for implementing the decisions.
Ground-level management is considered as the operational level.
Uncertain and dynamic decisions of the organization are to be taken at this higher level of management. The decisions regarding structured workflow, the foundation of distribution channels, etc. are taken at this level. The judgments regarding everyday operations and daily business activities are made at the operational level.
Unstructured decisions are taken at this level of organization. Semi-Structured decisions are taken at this level. Structured decisions are taken by the operational management level.
Decision Making Process
From a given set of available alternative scenarios, selecting a particular set of actions is regarded as the cognitive procedure of decision making (Decision Making Process, 2017). It is regarded as the complex procedures in the hierarchies present within management.
The process stepwise:-
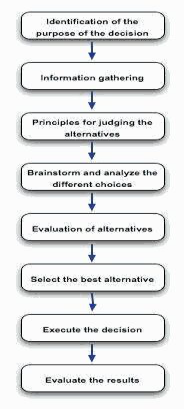
Figure 2: Decision-Making process
(Source: Decision Making Process, 2017)
Identifying the decision's purpose: Analyzation of the overall problem is done here.
Gathering of Information: Many stakeholders will usually come into consideration whenever an organization faces a problem. There is definitely a possibility of existing factors thereby affecting the problem. So, as a result, all sorts of information in accordance with various factors & stakeholders need to be gathered. ‘Check Sheet' tool could be used.
Judging the alternatives through principles: The criteria of baseline shall be utilized for this purpose. While the formulation of the criteria, along with corporate culture, goals of the organization should be considered as well.
Analyzing various available choices along with brainstorming: All the ideas have to noted down fir brainstorming. According to __, Cause-and-effect and Pareto Chart tools could be used prioritization of causes in accordance with the issue. This is the identification of all possible causes. On the other hand, the Pareto Chart helps in prioritizing the cause that too with the highest impact and effectiveness as well. After the prioritization, all the possible solutions should be generated.
Evaluating the alternatives: Under this step, the experience and judgmental principles are bein utilized and effective skills in them help in taking powerful and complex decisions as well.
The best-suited alternative is being selected in the sixth step.
Furthermore, in step 7, decisions finally undertaken are gradually converted into a plan or series of planned activities.
Executive Information System / Executive Support System
It is broadly defined as the specialized category of DSS. The different hardware, software, data, procedures along with people are generally included within this system. The top management level executives are able to take their decisions in an effective manner through great support provided by this system (Krutz and Vines, 2010). Data is able to be obtained from a wide variety of available sources through an executive information system.
Furthermore, it assists in integrating and aggregating this obtained data. After applying all these different steps, the resulting information is demonstrated further in an understandable format.
EIS accounts to be a computer-based system for serving the obtained information to different top-level executives. Very quick and easy access is provided through its help to the timely information. It also accounts to be user-friendly along with an enhanced level of graphics.
As stated by Galegher, Kraut and Egido, (2014), the Executive Support System showcases dependency upon the following factors :
Internal factors:-
- When necessary information is needed on a timely basis.
- When improvement in the communication process is required.
- When accessing the operational data is needed.
- When various status updates are made regarding different activities of a business.
- When accessing information regarding the corporate database is required.
- When accuracy in information is needed.
- When the identification of various historical trends has to be done.
External factors:-
- The enhancement and intensification of competition at a global level.
- The rapid changes occurring within the environment of business.
- Increased level of pro-activeness needed.
- When accessing an external database is needed.
- The increased pressure of rules & regulations by the government.
Characteristics of EIS:-
1. Informational Characteristics:-
- Quick responsiveness in providing timely information.
- Accurate, relevant and validated information is produced.
- It provides the flexibility of using (Ricci, Rokach and Shapira, 2011).
2. User Interface/Orientation Characteristics:-
- Helping oneself in a sophisticated manner.
- Graphics user is contained thereby offering a user-friendly interface.
- Utilization could be carried out from different locations.
- The access procedure towards information is securely reliable and confidential as well.
- Customization is at a very high level.
- The individual executives are the best-suited management style for it.
3. Managerial Characteristics:-
- The overall mission, vision along with strategy are given support.
- The support which is required for strategic management is given.
- Situations having high degrees of risk are dealt with its help.
- The value-added procedures of business are linked to it.
- It also provides the necessary support for accessing external data.
- Highly oriented toward getting outcomes.
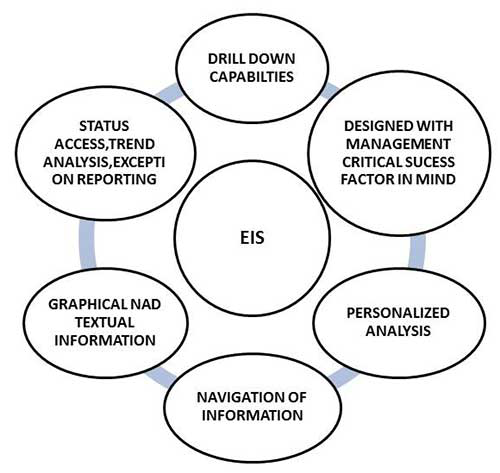
EIS Dashboard: The Executive Information System has been developed for analyzing and supervising the performance, trends, risks, and opportunities that are addressed by a business user and the decision-makers.
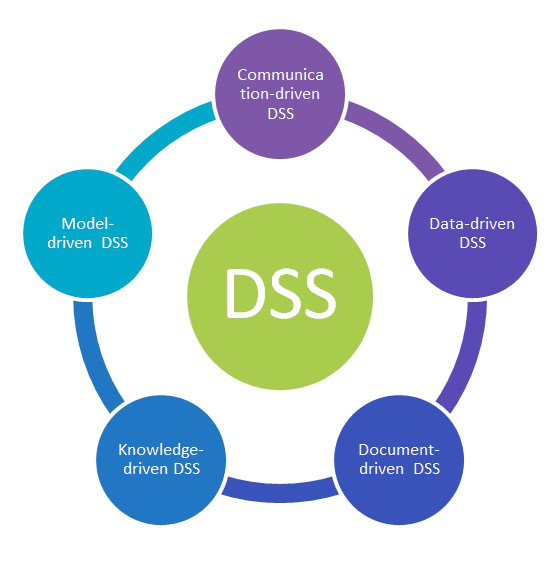
Decision Support System
With the aid of interactive software-based systems, the managers of organizations are able to carry their decision-making procedures. These interactive systems are broadly known as Decision Support Systems (Melville, 2010). The summaries, exception pattern, trend via models of analyzation are overall as a whole utilized by DSS. It is not intended to give a particular decision but rather supports decision-making. From the raw data, document, personal- knowledge along with business models are being utilized by decision-makers for identification and solution with respect to a particular problem and taking of the necessary decision.
Programmed and non-programmed decisions:-
General routine work along with automated procedures are included within programmed decisions:
- Such decisions have already been taken numerous times.
- These have to stick to a certain set of guidelines along with some rules as well.
- For example: Select a reordering level for the inventories.
Unusual situations involve taking up of non- programmed decisions.
- Always a brand new decision.
- No specific regulations are being considered.
- The information that is available accounts to be the basis of this decision.
- The discretion, perceptions, and instincts along with judgmental opinions possessed within a manager form a basis for these decisions.
- For example: to invest in a new technology comes under the non- programmed decision category.
Characteristics of DSS:-
- It provides flexibility and ease of adaptation because of the high level of inter-activeness.
- The users or customers are allowed to have control over the input and outputs.
- Negligible assistance is taken from the professionals in operating it.
- Difficult issues and situations are easily tackled by managers by getting quick solutions through this system.
Improving the Managerial Decision Making with the help of DSS
- The Intelligence Phase: The production of data occurs on a timely basis. The utilization of quantitative data is enhanced (Bulgurcu, Cavusoglu, and Benbasat, 2010). Moreover ample of data or information is made available to the managers for making decisions.
- The Designing Phase: The amount of alternatives available is in ample quantity and more accurate as well.
- The Choice Phase: The making of decisions occurs at a faster pace. Moreover, the choices made are further given a rank accordingly.
Transaction Processing System
The system involved in the processing of the business-related transactions is referred to as the Transaction Processing System(TPS). Within it, the data related to transactions is first collected and then modified accordingly for its retrieval (Structure, Activity, and Functions of Transaction Processing System, 2015). The performance, consistency along with reliability are included among the characteristics of TPS which is further known as real-time or transaction processing.
Processing Types:-
- Batch Processing: A series of programs are gradually executed without any interference manually on a computer. Numerous transactions or batch are gathered and accordingly processed at the same time. However, a time delay is observed in case of getting an outcome with respect to each transaction.
- Real-time Processing: The stimulus itself or the quick conditions causing it, are guaranteed an appropriate response from real-time systems. Every transaction is of a unique nature.
- Time-sharing: The computer system is being shared among multiple users. However, there always exists a certain set of regulations upon each user's type of work allotted.
Transaction Processing System functions
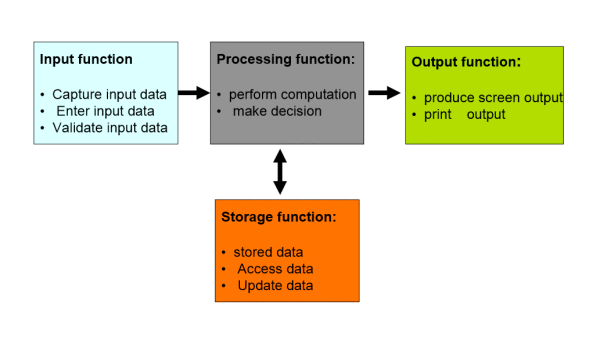
Figure 4: TPS
(Source: Structure, Activity, and Functions of Transaction Processing System, 2015)
Input, output, storage, and processing are included in some of the functions coming under the transaction processing system (Bélanger and Crossler, 2011).
- Input Function: Upon a source document data is first captured in the first step. Within the system, the input data is then entered. Data validation process is carried out for checking any sort of existing errors in input data.
- Output Function: In this, reports are being produced, for example, detail, summary or exception reports.
- Storage Function: Databases and files are utilized for storing data. The data which is stored can be further accessed, sorted and updated as well.
- Processing Function: The stored data can be further manipulated by either computing or making decisions (Gorla, Somers and Wong, 2010).
Conclusion
With context to the report, one thing is of uttermost significance that administration operations have to be effectively planned in an organization. These finance-based transactions are very much confidential and have to be managed in an effective manner. Transaction Processing Systems or TPS has to be implemented by the lower-level managers for maintaining a financial balance. Managing Information systems is an aid for middle-level managers to handle all sorts of decisions related to financial transactions. Decisions must be developed in a structured, unstructured or even semi-structured. Decision Support System has to be efficaciously and efficiently utilized by management authorities for making effective decisions. Higher-level management authorities should use EIS as a significant tool in developing effective decisions.
References
- Bélanger, F. and Crossler, R. E., 2011. Privacy in the digital age: a review of information privacy research in information systems.MIS quarterly.
- Bulgurcu, B., Cavusoglu, H. and Benbasat, I., 2010. Information security policy compliance: an empirical study of rationality-based beliefs and information security awareness.MIS quarterly.
- Dubois, É., Heymans, P., and Matuleviius, R., 2010. A systematic approach to defining the domain of information system security risk management. In intentional Perspectives on Information Systems Engineering
- Galegher, J., Kraut, R. E. and Egido, C., 2014.Intellectual teamwork: Social and technological foundations of cooperative work. Psychology Press.
- Gorla, N., Somers, T. M. and Wong, B., 2010. Organizational impact of system quality, information quality, and service quality.The Journal of Strategic Information Systems.
Also Read-


























