Electrochemical series or activityseries refers to a list which explains the arrangement of elements in order of their increasing potentialvalues. This series is established by measurement of potential of various electrodes Vs the standard hydrogen electrode (SHE).

The ions of different metals are arranged on the basis of their standard reduction and oxidation potentials. The tendency of one metal ion to reduce any other metal ion below shows the importance of electrochemical series.
The standardstatepotential of the cell is defined as the potential of the cell under the following conditions:
- Concentrations of 1 mole per litre (1 M).
- Pressures of 1 atmosphere.
- Temperature of 25 degrees Celsius.
Significance of the electrochemical series
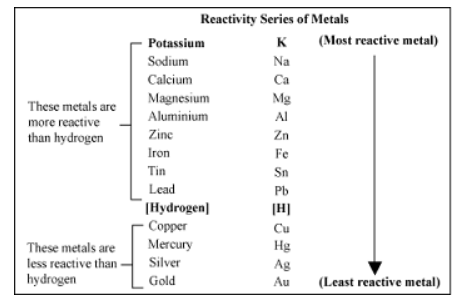
Figure1. Electrochemical series of metals
The electrochemical series is important as it helps in identification of the electronegativity andelectro-positivity of the element/ion combination in comparison to the standard hydrogen electrode.
An electronegative element derives an electron from an electropositive one. Therefore, electrochemical series is a measurement of electronegativity of an element.
You may also like to read about the related service - case study help
What is Potential difference (Max cell voltage)?
The standard half potential indicates the tendency of any metal to undergo reduction in a electrochemical series. Higher value of standard half potential states the occurrence of reduction reaction, on the other hand, lower value of standard half potential will indicate the occurrence of oxidation reaction.
Importance of electrochemical series
The electro-chemical series is an orderly arrangement of metal ions in an ascending order on the basis of their electrode potential. The importance of electrochemical series includes the identification of good oxidizing and reducing agents. The significance of electrochemical series is given as follows:
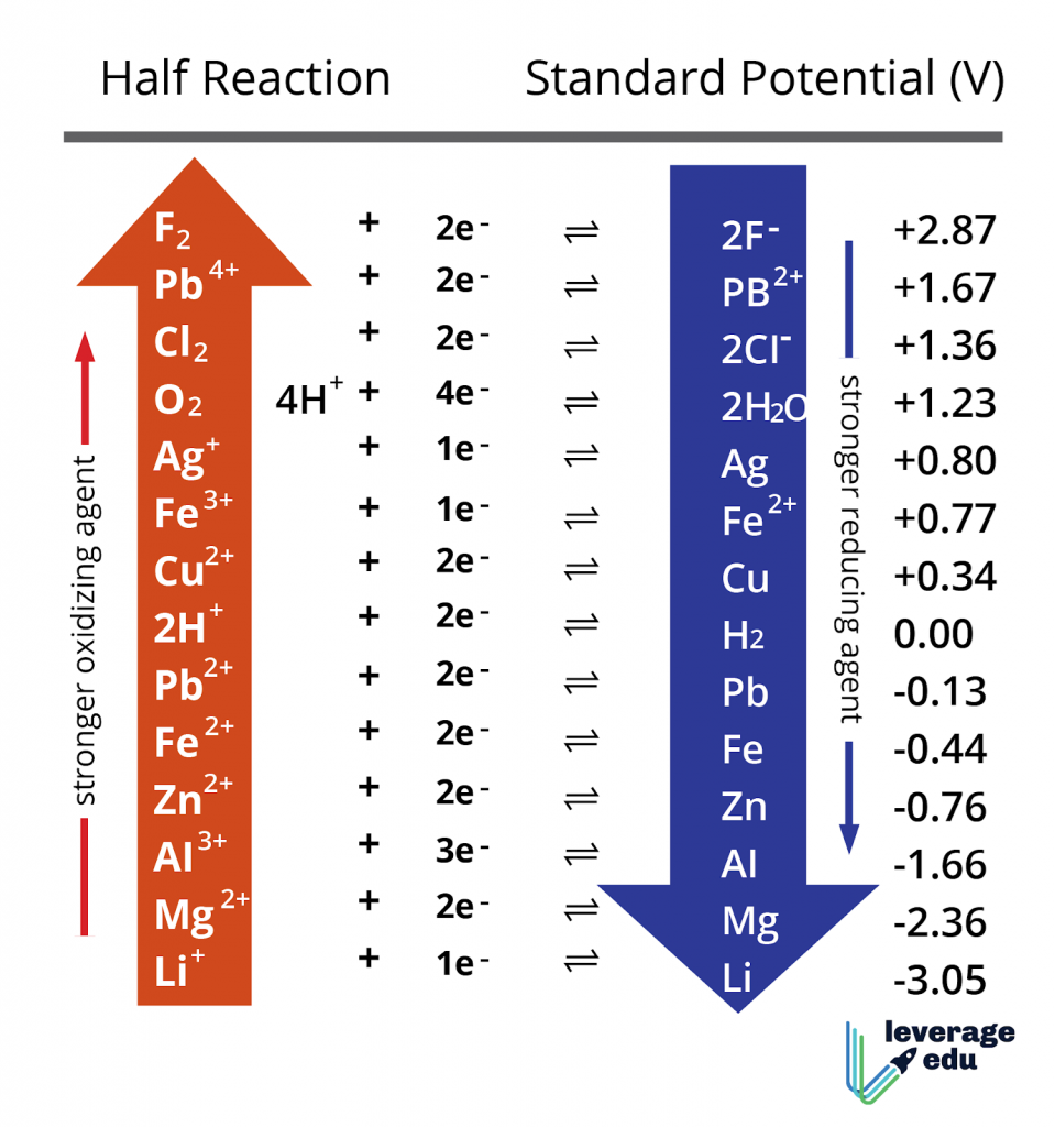
- The comparison of relative oxidizing and reducing strengths of various metal is possible through the application of electrochemical series.
In an electrochemical series, the metals are arranged in increasing order of their reductionpotential, in other words, the metals are arranged based on their strengths as an oxidizing agent. This information allows the students to select appropriate metals to use as oxidizing and reducing agents for completion of reaction.
- The relativeactivities of metals towards displacementreactions can be compared based on their placement in the activity series.
According to the electrochemical series, a metal which is placed higher in the series will replace the metal present below in its solution form. The metal placed higher has a tendency to impartelectrons to the cations of the precipitated metal.
- Prediction of the product of electrolysis
The metal ion liberated first during electrolysis is considered as a stronger oxidizingagent(shows a high value of standard reduction potential) which is discharged first at the cathode.
- The calculation of standard EMF of any electrochemical cell is possible.
The EMF or electro motive force of the cell is the difference of the standard potential of the cathode and the standard electrode potential of the anode.
E°cell= E°(cathode) – E°(anode)
If the EMF of the cell is positive, the reaction is proved to be feasible in the given direction. However, if the EMF of the cell is negative, the reaction is not feasible in the predicted direction. Negative value of E° signifies that the metal will lose electrons and the reducing agent will be stronger. However, positive value of E° will imply that the metal ion is more likely to pick up electrons, making it a stronger oxidising agent.
- Prediction of the feasibilityof the redox reaction.
The electrochemical series gives researchers an idea about the increasing order of electrodepotentialfor reduction for different electrodes as one moves down the table. This signifies that for species to accept electrons (reduced) must be present below the element getting oxidized in the electrochemical series.
- Anticipating the liberationofhydrogengas when a metal reacts with acid.
For example, a metal (M) reacts with an acid (H+) to give hydrogen gas-
M + H+———-> (M+) + 1/2H2
According to the electrochemical series, only metals with negative values of reduction potential (-E°) will liberate hydrogen gas. Therefore, reactive metals such as Zn, Mg will liberate hydrogen gas by-
M (Monovalent) ———> M+ (aq) + e_
H+ (aq) + e– ——> H or 1/2H2

The electrochemical series represents a thermodynamic argument where the metals at top of electrochemical series represent alkali or alkalineearthmetals, which are very easily oxidized. This implies that these metals can react easily to form compounds and are hence called active metals.
The metals present at the bottom of the series are called as “noble” metals, as they are very less reactive and hence are used to make coins and jewellery. These metals are also called as transition metals and are very stable.
The metals at the top are considered as good reducing agents whereas metal ions that are present at the bottom of the series act as good oxidising agents. The oxidising ability of the metal ions increase as one moves down the series, on the other hand, the reducing ability increases as we move up the series.
Frequently researched questions (FAQs)
QUESTION 1. What are the features of electrochemical series?
Ans. 1) The most important aspect of electrochemical series is that all the potentials values of elements are defined with respect to it. Half cells with positive electrode potential are strong oxidising agents whereas, half cells with negative electrode potential are termed as reducing agents.
QUESTION 2. What is an electrochemical series and how is it useful in predicting?
Ans. 2) The electrochemical series is a table where several electrodes are arranged in increasing order of their standard reduction potential values. The electrochemical series enables the students to predict whether or not a metal will liberate hydrogen upon reaction with acid.
QUESTION 3. What are the limitations of electrochemical series?
Ans. 3) The electrochemical series is unable to determine the rate of the reactions of halfequations. The prediction does not guarantee occurrence of the reaction. Also, if the preferred favourable conditions deviatetoo much, there is a possibility that the reaction will not occur at all.
QUESTION 4. What are the application of electrochemistry?
Ans. 4) There are many applications of electrochemistry in everyday life including use of batteries to power a flashlight, automobile and even a calculator. Chemicalreactions employed for the generation of electricity.
QUESTION 5. What is the easiest way to memorize an electrochemical series?
Ans. 5) “KINGS CAN NOT MAKE A ZEBRA. I LIKE HIS CAR'S SILVERY GATE”
Kings- POTASSIUM
Can- CALCIUM
Not- (NA)SODIUM
Make- MAGNESIUM
A - ALUMINIUM
Zebra- ZINC
I - IRON
Like- LEAD
H is- HYDROGEN
Car’s-COPPER
Silvery-SILVER
Gate- GOLD




















