“BREATHING IS A FRAGILE VESSEL THAT CARRIES US FROM BIRTH TO DEATH”
Respiration is a process through which all living organisms derived energy from organic substances. There is a breakdown of organic molecules into carbon dioxide and water. The energy produced by respiration is used for performing all the physiological functions in the body such as cell proliferation, cell repair, etc. The release of energy is step-wise and controlled which aids in cell metabolism.
Respiration ensures efficient conversation of energy and a total of 38 ATP molecules are saved. Most living organisms require oxygen for their survival which is taken up by the mouth and nose in humans. Oxygen causes the cells to break down food molecules and convert them into energy required for survival. There are different organs used by different animals to facilitate the process of acquiring oxygen through respiration.
However, breathing is the flow of air in and out of the lungs to facilitate the exchange of gases. In other words, the uptake of oxygen and flushing out of carbon dioxide. This process is also termed as pulmonary ventilation, which consists of two phases- inspiration (inhalation) and expiration (exhalation).
Oxygen is extremely crucial for the production of energy which acts as a fuel for conduction of living processes. Breathing involves use of certain chemical and mechanical processes which facilitate the transport of oxygen to each and every cell of the body. In humans and animals, carbon dioxide is a waste product of these chemical processes. This carbon dioxide is taken up by plants for production of their food through photosynthesis.
Also Use Our Free Grammar Checker Tool
The two steps of pulmonary ventilation (breathing) are:
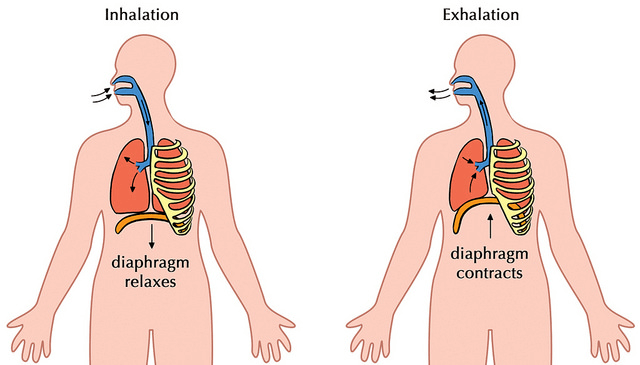
- Inspiration: This phase is characterized by the entry of airin the lungs. The diaphragm relaxes during inhalation of air. The lung pressure is reduced below the atmospheric pressure which facilitates entry of air into the lungs.
- Expiration: This phase is defined by the exit or flowing out of airfrom the lungs. The diaphragm contracts during exhalation of air. During expiration, the atmospheric pressure is reduced as compared to the lung pressure which pushes air out of the lungs.

Oxygen is crucial for occurrence of catabolic processes because of which carbon dioxide is released out of the body. The exchange of carbon dioxide produced by cells in the body with atmospheric oxygen takes place in the lungs which are also known as respiratory sites.
 The essential process of breathing involves inhalation of air from the atmosphere, where it reaches the lungs to facilitate the movement of oxygen to blood capillaries. Similarly, carbon dioxide diffuses from blood to the lungs making its way out of the body.
The essential process of breathing involves inhalation of air from the atmosphere, where it reaches the lungs to facilitate the movement of oxygen to blood capillaries. Similarly, carbon dioxide diffuses from blood to the lungs making its way out of the body.
Respiration is of two types: Aerobic respiration and Anaerobic respiration. Aerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration which takes place in the presence of oxygen. This process can be best explained based on the following equation:
⇒ Glucose(C6H12O6) + Oxygen(6O2) → Carbon dioxide (6CO2) + Water (6H2O) + Energy (ATP)
On the other hand, anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration which occurs in the absence of oxygen.
⇒ Glucose(C6H12O6) → Alcohol 2(C2H5O H) + Carbon dioxide 2(CO2) + Energy (ATP)
Red blood cells are present in blood surrounding the walls of alveoli which acts as a transport system for carrying oxygen to various part of the body. Carbon dioxide and oxygen are diffused between the respiratory system and circulates into the blood stream. The red blood cells attach themselves to oxygen molecules which makes its way to the heart and different parts of the body to facilitate smooth functioning.
Students also take assistance for: Case Study Help Online
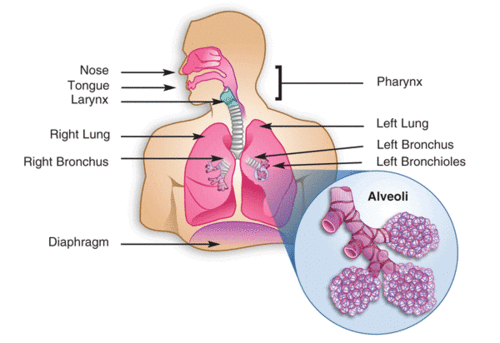
The process of respiration
The diaphragm contracts as atmospheric air is inhaled, the ribs move upwards and outwards which helps the chest cavity to grow in size in order to make space for air. This air is inhaled through nose and the lungs where it passes through epiglottis making its way to the trachea. The air moves to the bronchi, which branches out into the alveoli. Alveoli are tiny air sacs which are extensions of bronchi.
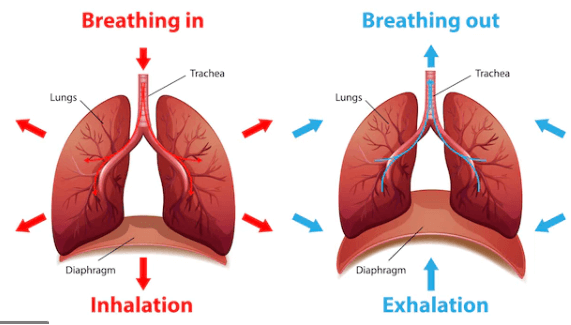
Alveoli are surrounded by blood capillaries which facilitate exchange of gases. Carbon dioxide diffuses out of the blood through process of diffusion followed by its expulsion through the lungs. Similarly, oxygen diffuses into the blood making its way to the cells to carry out cellular respiration.
Breathing is an important function which is essential for maintaining body/health connection. The proper functioning of body is highly dependent upon the availability of oxygen which helps enhances mental health, improves sleep cycle and reduces the stress levels. Availability of oxygen strengthens muscles in the body and increases body’s immune response making it less susceptible to contracting diseases.
Breathing facilitates the process of uptake of oxygen as per requirements of the body along with expelling all metabolic wastes. These chemical processes occur in mitochondria of the cell, otherwise known as the powerhouse of cell. The production of these energy rich compounds such as ATP (adenosine triphosphate) facilitates the breakdown of food molecules and acts as a precursor for other cellular processes.
Major differences between breathing and respiration
|
Category |
Breathing |
Respiration |
|
Definition |
Breathing is the process of inhaling oxygen and exhaling carbon dioxide. |
Respiration is the process of breakdown of glucose which is required in energy production. |
|
Occurrence |
Breathing takes place in the lungs. |
Respiration takes place in cells. |
|
Type of process |
Breathing is a voluntary physical process. |
Respiration is an involuntary chemical process. |
|
ATP production |
No production of ATP. |
Energy is released in the form of ATP. |
|
Cellular activity |
Extracellular process as it occurs outside cells. |
Intracellular process as it occurs inside the cells. |
|
Usage of enzymes |
There are no enzymes used in this process. |
There are a lot of enzymes employed in this process. |
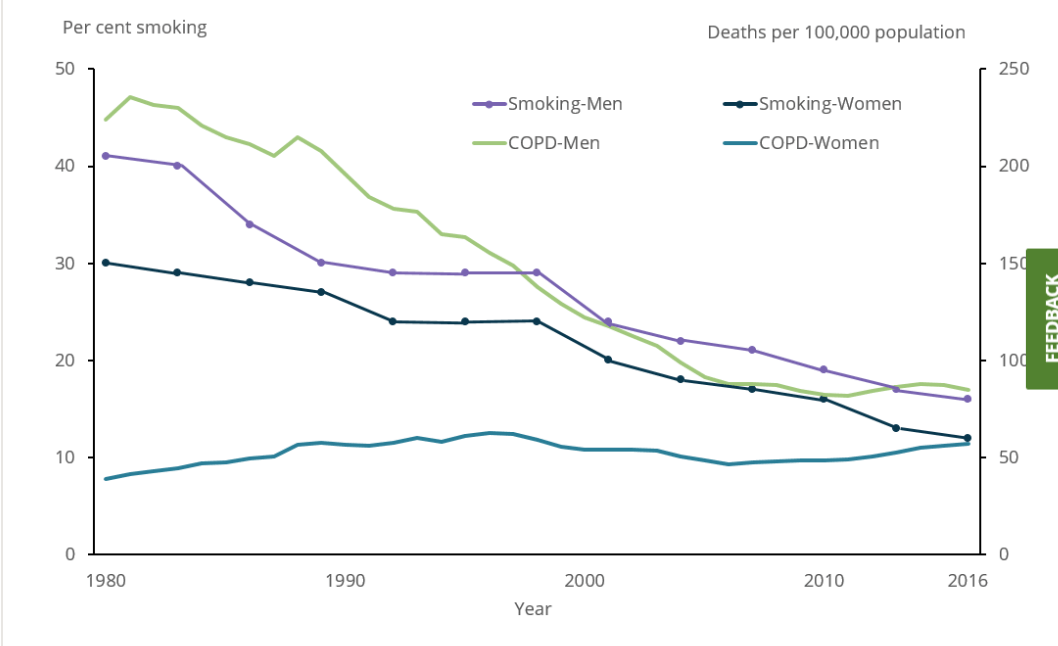
Disruption in functioning of normal respiration leads to development of chronic respiratory diseases. Two major chronic respiratory diseases prevalent in Australia are asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It is safe to say COPD is a major cause of death in Australia.
COMMONLY ASKED QUESTIONS or (CAQs)
Question1. How are breathing and respiration related?
Ans.1) Breathing is also called as respiration as the oxygen is inhaled through lungs and carbon dioxide is exhaled out of the body. Cellular respiration involves the breakdown of larger glucose molecules into ATP for the release of energy.
Question 2. Does respiration mean breathing?
Ans.2) Breathing is an act of inhaling and exhaling of atmospheric air in and out of the body whereas respiration is the process of breakdown of sugar for production of energy.
Question 3. Why is respiration so important?
Ans.3) Respiration ensures the supply of oxygen into the body and the removal of carbon dioxide out of the body which satisfy the adequate metabolic needs of the cells.