Introdution
Organisational behaviour is related to the individuals behaviours and activities in the organisation such as – predicting, understanding, etc. It is all about employees working in the organisation – how they act or behave, how they perform daily operations and how they deal with different situations at workplace (Bolino and et. al., 2013). Marks and Spencer which is a British international company established in 1884 has been taken in this report. Impact of organisational, culture, power and politics on employees and overall structure is also explained. Further, content theory and process theory of motivation to motivate individuals is described in this project. Effective team and how it is better from ineffective team is also mentioned. Philosophies and concepts on organisational behaviour in administration is also explained.
TASK 1
P1 Influence of organisational power, politics and culture on organisation
Culture, politics and power play an important role in any organisation, as all these components impacts daily operations and regulate the environment within the workplace. Impact of politics, power and culture instantly affect the structure of organisation. In context to Marks and Spencer it affects components of organisational structure which are – centralisation, chain of command, decentralisation, work specialisation, span of controls and departmentalization.
Students having trouble in writing their essays, can easily opt for our Essay Help UK from Ph.D writers.
Organisation culture
In every organisation there is different culture. Different types of employees have different backgrounds, values, beliefs, customs, traditions, etc. Organisation culture refers to the assumptions, beliefs and values which determines how individuals act at the workplace. In context to Marks and Spencer – the company has unique culture which gives outlines and guidelines for the activities of individuals in the organisation. To define culture in Marks and Spencer Handy's typology has been used which is explained below (Carpenter, Berry and Houston, 2014).
Handy's typology
- Power culture:- In power culture individuals and their performance is judged on the basis of result of their work done by them. Power is given to few people in the organisation and all decisions are taken by them, which can be both pleasing and adverse for the administration. It is strong culture and can quickly turn toxic.
- Task culture:- Task culture takes place in an organisation when group of individuals come together or a team is formed to solve particular problems of common projects and to complete it. Task is very crucial, so power in the group will frequently change depending on the unit members and project status (Chance, 2013). Task culture will be effective if, individuals work together with good skills, leadership and personalities.
- Role culture:- In role culture organisations are based on regulations. They are controlled by everyone in the administration identifying about their roles and obligations. Power in this type of culture is defined by an individual's position in structure of the organisation. Having role culture in the organisation will make business bureaucratic.
- Person culture:- In person culture individuals feel themselves superior instead of organisation. They are concerned with their own feelings and work at the workplace. Having person culture in the organisation is actually just aggregation of individuals who go on to be working for the identical organisation.
In context to Marks and Spencer task culture will be mote effective as it help in performing assigned projects or task by working together and solving issues related to that task. It also help in identifying individuals with good skills and knowledge.
Organisational power
In an organisation power refers to the ability which influence individuals and overall working of the administration. Power is advantageous in Marks and Spencer when managers provide different task to individuals and encourage them to complete those assigned projects. It is their responsibility to guide and provide directions to them, for achieving organisational goals (Fisher and To, 2012. French and Raven's five types of power are explained to describe power in the organisation.
- Reward power:- It is the common power among different powers. Reward power refers to the ability to provide something in return of their work or performance of individual or asking them about their requirements for the desired work. It involves incentives, bonuses, appreciations, new opportunities, etc. for good work done and sometimes punishment for poor work. Providing rewards to employees in the organisation will motivate them.
- Expert power:- Expert power refers to skills, knowledge and qualities of an individual which is required by someone else in the organisation. Having expert power in the organisation will help in completing different tasks which requires various skills and qualities.
- Legitimate power:- Legitimate power refers comes from any title or position given to an individual in the organisation. It includes persons having positions like – CEO, Owner, Executive and other higher positions in the organisation.
- Coercive power:- It is just opposite to the reward power. In this power individuals are forced to do work without their wishes (French and Holden, 2012). Having coercive power will demotivate employees in the organisation.
- Referent power:- People having referent power are liked by others and have many qualities like – good skills, knowledge, attributes, attitude, behaviours etc. Having referent power in the organisation will influence everyone.
In context to M&S referent power will be effective as, it has great influence on the overall organisation.
Organisational politics
Politics refers to the use of power in the organisation to attain different changes which are beneficial for the administration. It can be informal and formal. Effective politics assist an organisation in improving employees relations and improve their performance. While unhealthy politics lead to demotivation of individuals and increases conflicts in the organisation.
Student should definitely take assignment help Uk from expert writers if they are too busy to complete their assignments on time.
TASK 2
P2 Process theory and content theory of motivation
Motivation is the inward process which encourages individuals to perform their roles and responsibilities, in order to attain desired goals and objectives. It is very important to motivate individuals in Marks and Spencer to accomplish organisational objectives. Here both content and process theory of motivation are explained under.
Content theory
There are various content theories of motivation. Maslow's hierarchy of needs is taken in Marks and Spencer to motivate individuals.
Maslow's theory of motivation
This theory was developed by Abraham Maslow in 1943. In this theory individuals tries to fulfil higher needs when lower needs are satisfied (Greenberg, ed., 2013). It is categorised into five different needs.
- Physiological needs:- Physiological needs include basic needs which are – food, shelter, air, cloth and water. These are the needs which are essential for human beings to survive. So according to Maslow it is important to satisfy these needs before others. In context to Marks and Spencer the managers should provide proper salary to employees, so they can fill their basic needs.
- Safety needs:- Safety needs involve environmental, physical and emotional protection. It means employees should provide proper security and protection in the organisation (Harms and Luthans, 2012). It includes – financial security, family security, job security, health security, protection from fear, etc. In context to Marks and Spencer the manager should provide good working environment, job security, pension, medical facility and retirement benefits.
- Social needs:- Social needs involve friendship, affection, trust, need for love, concern, acceptance, etc. It is the third level of hierarchical needs after safety needs. In context to Marks and Spencer the manager should provide opportunities to individuals to work together and organise social programmes in the organisation.
- Esteem needs:- Esteem needs involves two types of needs which are – self-esteem and external esteem. Self-esteem needs are – self-respect, competence, freedom, confidence and achievement. While external esteem needs are power, attention, recognition, admiration and status. In context to Marks and Spencer the manager should provide awards on achieving their targets and promote them to higher positions in the administration.
- Self-actualisation needs:- Self-actualisation needs involve requirements for higher growth, creativity, social service, self-contentment, etc. It is highest level of Maslow's hierarchy of needs. In Marks and Spencer the manager should offer challenging tasks to employees so they can utilise their skills and talent and attain higher growth.
Process theory
Process theory is a method of ideas which describes how an organisation develops and changes. There are different process theories of motivation. Vroom's expectancy theory is describes here.
Vroom's expectancy theory
This theory was developed by Victor Vroom in 1964. It concentrates on results instead of needs, in the organisation (Miao, and et. al., 2013). This theory involves three different variables which are – instrumentality, expectancy and valence.
- Expectancy:- Expectancy refers to the belief that doing any work with more efforts will improve performance. It means that hard working lead to effective or better outcome. In context to M&S employees can be motivated in the organisation by having appropriate resources, higher skills to perform a job and support which is necessary to complete the job.
- Instrumentality:- Instrumentality defines that if employees perform best, they will get beneficial and valuable outcome. It is impacted by various things – proper understanding about result and performance relations, trust on people who decide and declare the result and process clearness which decides outcome of everyone (Miner, 2015).
- Valence:- Valency is the importance related to an individual about the desired result. It is that result which is expected by the individual and not the actual outcome which the individual expects after accomplishing objectives.
In context to Marks and Spencer the manager should provide rewards to best employees, interrelate the preferred results with the decided performance levels, and give challenging or dynamic jobs to motivate employees.
TASK 3
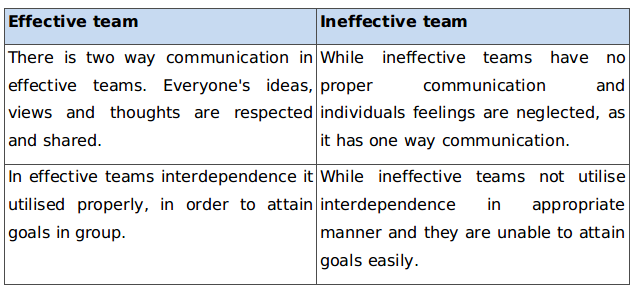
P3 Effective team in opposed to ineffective team
Team refers to group of employees in an organisation working together for goal accomplishment (Moore and et. al., 2012). It can be formed with individuals having good quality, skills and knowledge.
Effective team versus ineffective team
Types of teams
In Marks and Spencer different types of teams are formed to perform various tasks and achieve desired goals in the organisation. These teams are mentioned below.
- Project team:- Project team involves members with different groups or roles and are given work for similar projects or tasks in the organisation. These teams are formed for a limited time and are discharged after the task is finished (Morgeson and et. al., 2013). In context to M&S project team will help in solving problems related to various projects.
- Virtual team:- In virtual teams individuals communicate digitally with one another. This type of team is formed having different people from different places such as other cities or countries. Information is shared through telecommunications from other locations. In context to M&S virtual team will help in attaining organisational objectives with the help of people from different places.
- Functional team:- Functional teams are formed in the organisation to perform different functions of similar projects, in order to attain common goals. It involves individuals from different departments such as – marketing, finance, human resource, etc. In context to M&S functional team will help in attaining common goals by performing various functions.
- Problem solving team:- Problem solving teams are formed to solve particular issues in the organisation. These types of teams comes together to provide appropriate solutions to assigned tasks and projects in the organisation. These teams are formed for a temporary period, as their purpose is to solve specific problems. In M&S these problem solving team will assist in solving task related issues.
Tuckman's model of team development
Team development is essential to attain organisational objectives in the organisation. This model was developed by Bruce Tuckman in 1965. This model is used in M&S to motivate individuals. It involves five stages.
- Forming:- It is the initial stage of team development. In first stage individuals have no information about each other and their goals or objectives. They introduce to each other and communicate about their skills, talent and qualities. In Marks and Spencer this stage will help in knowing individuals about one another and their objectives.
- Storming:- At storming stage members consider each other as their part of team. Conflicts arise between individuals due to having different, ideas, thoughts and skills (Pinder, 2014). In context to Marks and Spencer storming stage may satisfy employees and it can also lead to dissatisfaction as there are many challenges in front of them.
- Norming:- In norming phase individuals come together, establish roles and responsibilities, develop processes, etc. In context to Marks and Spencer norming stage will help individuals to understand their obligations and how to perform the given tasks. It brings employees together to achieve desired goals.
- Performing:- At performing stage individuals focus on their tasks and respect everyone's ideas and thoughts. Now they don't compete with one another and work together (Podsakoff and House, 2013). In context to Marks and Spencer performing stage will assist individuals in working together to achieve desired targets.
- Adjourning:- It is the last stage of team development. At this phase projects are completed and objectives are accomplished. Now the team is dissolved and individuals move to new tasks. In Marks and Spencer adjourning phase will assist in discharging employees from the assigned task.
TASK 4
P4 Concepts and philosophies of organisational behaviour
Organisational behaviour concepts:- Organisational behaviour is based on different fundamental concepts which involves behaviours of both organisation and individuals. It is mainly categorised in two elements – individuals nature and organisation nature. Nature of individuals include basic qualities (Miner, 2015). Nature of employees is affected by different factors in the organisation such as – perception, individual difference, value of a person, motivation, etc. While nature of organisation defines its business objectives, employees standards, etc. Factors which affect the organisation's nature are – mutual interest, social system and ethics.
Philosophies of organisational behaviour (Path goal theory)
Path goal theory of leadership was developed by Robert J. House in 1971. This theory is supported by Vroom's expectancy theory. It defines a leader's behaviour which is best for the individuals and suitable for the situation or organisational environment to accomplish prescribed objectives. In context to Marks and Spencer the objective of applying path goal theory is to improve individuals empowerment, satisfaction and motivations, in order to increase their efficiency and make them productive. With the help of this theory employees are inspired through leaders and and perform best as according to the directions provided to achieve desired goals. It involves three steps by which it motivate individuals in the organisation which are explained under.
Determining individuals and characteristics of environment
The first step in path goal theory is to determine employees and environment characteristics in which the organisation is operating (Pinder, 2014). The leaders should identify members needs and requirements. Determining employees needs will make them happy as they are valued in the organisation. Further the leader should determine environmental features by considering following points in M&S.
- Task design:- The leader should determine that whether the task is complicated or not. In context to M&S if there the leader should support in both easy and ambiguous tasks.
- Formal authority system:- According to task authority clear goals should be provided to employees by the leader. In M&S the leader should provide transparent goals to employees.
- Work group:- The leader should provide proper support and cohesiveness in case of non-supportive team. In M&s the leader should be devoted to their team, in order to attain desired goals.
Selecting a leadership style
After identifying environment and employees characteristics the second step is to select a leadership behaviour to motivate and support individuals in M&S. The leader can use four styles of leadership.
- Directive:- In directive style the leader guides employees and provide direction to them – how to achieve the goals and in a efficient manner. In M&S the leader can use directive behaviour of leadership to guide and direct individuals.
- Supportive:- Supportive leadership style determines that the leader should provide proper support to individuals and provide a pleasing working environment. In context to M&S the leader should be concerned with the employees (French and Holden, 2012).
- Participative:- In participative style the leader involves individuals in their decision making process. In M&S the leader should provide opportunities to employees to participate in their work.
- Achievement:- Achievement oriented style set challenging objectives for individuals and encourage them to perform better. In M&S the leader should give challenging tasks to employees and motivate them to perform best.
Motivational factors
It is the last step in path goal theory to motivate individuals. In context to M&S the leader should define proper goals to employees. Clear paths must be provide to them, in order to attain goals easily (Chance, 2013). The leader should remove all hurdles, obstacles and hindrances occur in goal accomplishment. Lastly, employees must be provided proper support to complete the given tasks and achieve organisational goals. Avail essay help services from top writing experts in usa
Also Check:
Business Management Dissertation Topics
Receive Effective and Engaging Homework Help from Anywhere
Looking for Best Online Coursework Help US
CONCLUSION
It is concluded from the above project report that organisation power, politics and culture are very essential and influence an organisation both negatively and positively. Content theory and process theory motivates employees in the organisation and encourage them to accomplish prescribed goals. Further, different team assist in performing various operations in the administration. Concepts and philosophies to organisation behaviour assist in motivating employees.
Related Free Tools: Essay Typer USA
References
- Bolino, M.C., and et. al., 2013. Exploring the dark side of organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior.
- Carpenter, N.C., Berry, C.M. and Houston, L., 2014. Analytic comparison of self reported and other reported organizational citizenship behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior.
- Chance, P., 2013. Introduction to educational leadership & organizational behavior. Routledge.
- Fisher, C.D. and To, M.L., 2012. Using experience sampling methodology in organizational behavior. Journal of Organizational Behavior.
- French, S.L. and Holden, T.Q., 2012. Positive organizational behavior: A buffer for bad news. Business Communication Quarterly.
- Greenberg, J. ed., 2013. Organizational behaviour: The state of the science. Routledge.
- Harms, P.D. and Luthans, F., 2012. Measuring implicit psychological constructs in organizational behavior: An example using psychological capital. Journal of Organizational Behavior.
- Miao, Q., and et. al., 2013. The relationship between ethical leadership and unethical pro-organizational behavior: Linear or curvilinear effects?. Journal of business ethics.
- Miner, J.B., 2015. Organizational behavior 1: Essential theories of motivation and leadership. Routledge.
- Moore, C., and et. al., 2012. Why employees do bad things: Moral disengagement and unethical organizational behavior. Personnel Psychology.
- Morgeson, F.P., and et. al., 2013. Extending corporate social responsibility research to the human resource management and organizational behavior domains: A look to the future. Personnel Psychology.
- Pinder, C.C., 2014. Work motivation in organizational behavior. Psychology Press.
- Podsakoff, P.M. and House, R.J., 2013. Leadership effectiveness: Past perspectives and future directions for research. In Organizational behavior Routledge.



















