Question :
This assessment will cover the following questions:
- Explain venture type range which can be considered as the entrepreneurial.
- Evaluation of effects of small business economy.
- Generate important facets of the entrepreneur mindsets.
- Evaluation of environment which affects and hinder entrepreneurship.
Answer :
INTRODUCTION
Entrepreneur is an individual who owns a small business, manages employees and tolerates risks with an aim of earning profits and meeting customer’s needs. Entrepreneurship is the process of planning, introducing and operating a new small business (Zelekha, Yaakobi and Avnimelech, 2018). Small businesses are independently or privately owned as well as operated firms, which have limited size, employees and revenue depending on the industry. The report on entrepreneurship and small business management explores and illustrates range of entrepreneurial ventures and assesses impact of small business on UK’s economy. It will also study and determine the main aspects of entrepreneurial mind-sets and different environments that foster or hinder entrepreneurship.
TASK 1
P1. Types of entrepreneurial ventures and their relation with typology of entrepreneurship
The typology of entrepreneurs based on previous occupational backgrounds ( Ryu and Kim, 2018). Thus, It defines the capacity and willingness to develop, organise and manage the business venture on it risk so that profitability can be enhanced. He is the individual person who works as to undertakes the creation, organisation, ownership and risk of business. Thus, the typologies has been discussed in below contexted manner as-
Scalable start up entrepreneurship: These are the measurable start ups that are been set by an entrepreneur with a vision and mission statement of providing high quality services to their customers. They have a good approach of investors and venture capitalists that will help in generations a good amount of revenue for a nation. They operate within a cluster and attract almost all the risk factors as well as good amount of benefits that will help in effective expansion of business operations. The profit or revenue generated by them is utilized for expansion purpose by the firm.
Large business / established companies / Scalable enterprises: These are large businesses, which are setup with the motive of earning huge profits by way of creating long-term goals with proper planning. This kind of entrepreneurship consists of several owners and shareholders or investors and funds for operating business is obtained through venture capital, angel funding, bank loans etc. It is a recognized firm or entrepreneurship that employs more than 500 people with the goal of generating substantial revenue and profit for company and its shareholders (Rana and Nipa, 2019).
Small business entrepreneurship: This is an independently owned and managed for profit enterprise with a goal of growing into a long-term business that is profitable and sustainable (Nikolaou, Tasopoulou and Tsagarakis, 2018 ). It is a start-up commercial enterprise, which comprises of small firms that hire family members or local employees for operating business activities with fewer resources and investment. Street food vendors, Restaurants, Retail stores, Construction firms, Agriculture etc. are some examples of such kind of entrepreneurship.
Social entrepreneurship: they are known as the voluntary firm and thus, improves the overall operations and action plans within an organisation that works for the betterment and goodwill of people. Their major aim is to improve living condition of their customers. The profit generated is been used to carry out more extensive research and develop high quality products.
Typology of entrepreneurship
Social good organizations / businesses: It is a business built on innovative solutions and desires to make the world a better place with a goal to maximize impact in a sustainable way. This kind of entrepreneurial venture is setup with the aim of providing services to improve the lives and solve health as well as social issues. NGO’s, Non-profit organizations etc. are such kind of entrepreneurship (Frederick, O'Connor and Kuratko, 2018). Capital is generated through donations, charities and investments done by individuals or organizations that would like to contribute towards the society.
Serial entrepreneurship: These free enterprise's comes up with new ideas and starts businesses ad success is measured by the duration over the operations. This is an opposition to an entrepreneur who starts single business and runs daily operations of it until retirement.
Female entrepreneurship: This is the process where women organizes all factors of production, bears risks and provide employment to others in the society. Female entrepreneurship makes significant contributions to the economic growth and to poverty reduction.
Conclusion
Hence, It can be concluded that types of entrepreneurial ventures and entrepreneurship is closely related as it helps to drive out the operations which are been taken in consideration by the firm. The good approaches works as to set up suitable entrepreneurial venture and expand their business operations. Thus, it can be concluded that entrepreneurial practices are very diversifying and becomes more complex at the astounding rate.
Related Service - Write my Essay
P2. Similarities and differences between entrepreneurial ventures
Similarities between entrepreneurial ventures:
- Entrepreneurial ventures are established with a purpose of generating profits by performing business activities such as providing good and services to customers.
- Every business involves risks, which are inevitable (Aquino, Lück and Schänzel, 2018).
- Process of raising funds or capital are almost similar in every entrepreneurial ventures which usually consists of personal savings, bank loans, government grants, borrowings from financial institutions, family or friends etc.
- The main success behind every business enterprise is its talented and skilled employees who works towards success and achieving goals of the business.
- All entrepreneurs have capabilities and skills to setup their respective business organization by implementing the acquired knowledge, competencies and experiences.
Difference between entrepreneurial ventures:
|
Basis of comparison |
Micro entrepreneurship |
Small entrepreneurship |
Medium entrepreneurship |
Large entrepreneurship |
|
Meaning |
It is a small business started with a minor amount of capital, which is specialized in rendering goods and services for their local areas. |
This is a firm, which is owned and managed solely by an individual, which has a limited size and revenue with an annual turnover of more than 75crores. |
This type of business is seen as small and medium sized business, which have an annual turnover not exceeding 50 million (Ahmadian and Abdolmaleki, 2018). |
Large entrepreneurship is an organization or business, which is set up with defined goals and has an annual turnover more than 1.5 billion. |
|
Scope |
It is a low income generated entrepreneurial venture with very little possibility (Ahmadian and Abdolmaleki, 2018 Aquino, Lück and Schänzel, 2018 Frederick, O'Connor and Kuratko, 2018). |
Small entrepreneurship ventures have low or moderate scope as entrepreneurs may earn high revenues and profits in future. |
It has a fair scope of growth as the business already generates good amounts of profits, which can be used for developments. |
These entrepreneurial ventures have a huge scope of advancement and can expand at the same time while earning enormous profits. |
|
Goals |
Micro entrepreneurship have short term goals due to which less planning is required. |
These enterprises have short to medium goals or plans according to the necessities. |
Medium entrepreneurial ventures makes long-term goals with proper planning. |
Large enterprises have long-term goals or targets, which are formed through accurate strategic planning. |
|
Profits |
These enterprises earn ample profits, which is enough to support a living for the entrepreneur. |
These ventures produces moderate amount of profits through revenues. |
Medium entrepreneurial ventures makes reasonable amounts of profits. |
Large enterprises generates huge profits, which are distributed among the shareholders proportionally (Spigel and Harrison, 2018). |
|
Risks |
Due to small or limited business operations, the risk involved in micro entrepreneurship is little or low. |
Small entrepreneurship involves low or less risks because the activities of business are generally conducted in a small level. |
Medium entrepreneurial ventures comprises moderate level of risks due to high level of business activities. |
Large entrepreneurial ventures consists of very high risks as business operations are performed and conducted in a global or international level. |
|
Size |
This type of entrepreneurial ventures is diminutive in size due to fewer business activities (Kocollari and et.al., 2018). The operations are usually conducted within a region or city. |
Small entrepreneurial ventures are little and business operations are done across cities or areas. It includes products and services, which are created for a particular community. |
These are moderate sized entrepreneurial ventures and its operations are carried out throughout cities and states. |
These are big entrepreneurial ventures, which involves huge amounts of business activities, and operations that are performed in a large scale. |
|
Number of employees |
Micro enterprises employs fewer than 10 employees. |
Small enterprises have up to 50 employees. |
Medium sized enterprises works with maximum of 250 or fewer employees. |
Large entrepreneurial ventures hire more than 500 employees. |
M1 Find and present the facts of entrepreneurship in public sector
Public sector entrepreneurship is a collaboration of an entrepreneurial start up with a public sector firm or government that woks for a larger population (Zelekha, Yaakobi and Avnimelech, 2018). They utilize their innovation and technical skills to improve the economic conditions and cater a larger customer base. It will help in proper evaluation of customer's needs and demands to have a good revenue generation.
D1 Critically examine the development and growth of entrepreneurial ventures
The entrepreneurial ventures will help in proper assessment of the growth measures that are taken within the organisation and thus will lead the firm to improve the quality of services and products offered by an entrepreneurial venture. At the initial stage, suitable business idea is been identified that helps the firm to improve quality of services and thus, will lead the firm to analyse the needs and demands of an entrepreneurial ventures and thus, will help in appropriate planning of operations that will help in planning of innovative products and services and meeting requirements of their buyers.
TASK 2
P3. Statistical data evidences on how micro and small businesses impact on UK’s economy
Micro and small business are the central pillar of UK’s economy where 99% of firms are SME’s. Small businesses contribute positively to growth and innovation.
As per the statistical analysis of businesses in UK, the following are obtained:
- Identified businesses in UK in the year 2017 were 5.7 million which increased by 197,000 or 4% since 2016 and 2.2 million more than in 2000 (Scarborough, 2016).
- Small scale enterprises have increased by 2%(128,000 and 76,000)
SME’s and the UK economy
- Out of the 99% of businesses, 5.5 million were micro-industries which accounted 33% of employment and 22% turnover (Schaper and et.al., 2014).
- Total employment generated in SME’s was 16.1 million; 60% of all private sector occupations in United Kingdom (BUSINESS POPULATION ESTIMATES FOR THE UK AND REGIONS, 2017)
- The combined annual turnover of SME’s was £1.9 trillion, 51% of all private sector turnover in UK
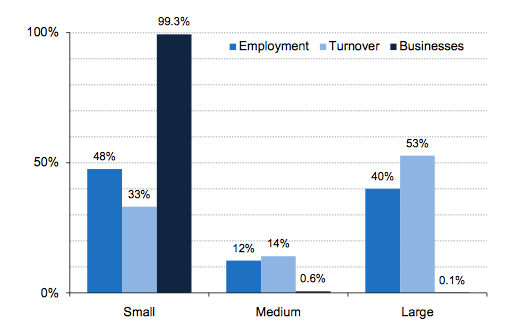
Illustration: Growth of SME’s in UK
(Source: Essential Facts You Should Know About SMEs in the UK, 2017)
Business population composition
- There were 1.3 million employing businesses in 2017, where 76% did not employ anyone aside from the entrepreneurs
- There are 3.4 million sole proprietorships, which covers the 60% of total, 1.9 million companies and 414,000 partnerships (Stokes, Wilson and Wilson, 2010).
Trends in business population
- Sustained growth in the total business population increased by 197,000(+4%) since 2016 and was 2.2 million in 2000.
- The majority of business population growth was due to the non-employing businesses, which accounted for 89%.
- There were 34,000 medium sized businesses with 50 to 249 employees of the total business population.
Registration for VAT and PAYE
- 3.1 million Businesses (55%) traded without being registered for VAT or PAYE and were classified as unregistered (Akehurst, Simarro and MasTur, 2012).
- 14% of sole proprietorships and 52% of partnerships were registered for VAT or PAYE
- National statistics recorded 2.6 million private sector businesses as registered for VAT or PAYE which is 45% of the estimated total population (BUSINESS POPULATION ESTIMATES FOR THE UK AND REGIONS, 2017).
UK economy has contributed widely by the service sectors towards GDP, which has raised from 59% to 72% over last three decades. Growing importance of SME’s within industries of western economies has resulted in various developments in UK’s economy. The turnover of this entrepreneurial venture amounted to £25 to £500 million depending on the scale of operations. However, many SMEs have faced challenges and difficulties due to Brexit, which led them to shutdown business operations. The remaining small and micro enterprises coped with hitches and stayed stable which have conquered UK’s economy.
Whereas, some SME’s have also contributed positively to the economy by trading internationally that led to globalization and high economic growth (Alsos, Carter and Ljunggren, 2011. The government of UK has been taking several initiatives to assist micro and small businesses to prosper in country, which has helped SME’s to become one among largest economies globally. Supporting SME’s and start-ups are essential for UK’s economy for innovation and progress. Due to this reason, government may potentially cooperate with banks and financial institutions to aid lending processes, which can be done by making realistic requirements. This will help business start-ups when applying for loans and grants. Innovation, employment and adaptability are the major contributions that SME’s have made to London’s economy and acts as a driving force for new innovations. SME’s also helps to make UK more attractive and competitive to investors and tourists as it increases diversity and variety in serving the communities in which they are based.
SME’s bring the tax burden down thereby encourages investment and spending considering simplification of tax reliefs. It impacts on the UK economy by tackling production issues which is a major issue of employees and companies in UK. Globalization has allowed SME’s to do more of their own specialized manufacturing at low cost and high accuracy in UK rather having outsourced production to lower cost countries in markets that are developing.
P4. Contribution of small businesses and start-ups to the growth of social economy after Brexit
Small business of UK has been facing an uncertain future ever since the UK’s referendum decision to leave European Union (Blackburn, Hart, and Wainwright, 2013). Yet, there is a growing judgement that wealth generated of SME’s might be leading charge into the economic level of UK at a consumer level. SME’s are the lifeblood of UK’s economy, which has a wide impact on country’s GDP generation. However, UK’s economy had seen a 0.5% decline in growth rate and GDP after Brexit, which has affected negatively the larger entrepreneurial ventures as compared to micro enterprises. High growth SME’s or Gazelles as they’re also known as are growing by 20% according to the investigation conducted by Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development.
One of the positive outcomes of Brexit to SME has noted an upturn in business, as 37% of these energetic start-ups were able to attract new customers as well as manage existing sales without much hurdles (Saebi, Foss and Linder, 2019). It has led to an export flourishing which resulted due to the deflation of pound value, competitive prices that ensued overseas investments. Start-ups, small businesses or micro enterprises have a significant contribution to the UK economy, as these are major platforms of job creation. Official data shows that retail industry is the largest SME employer in the private sector. As per the findings of Centre for Economics and Business Research, SME sector’s businesses contributes £196 billion to UK’s economy, which will continue to grow by 11% till 2020.
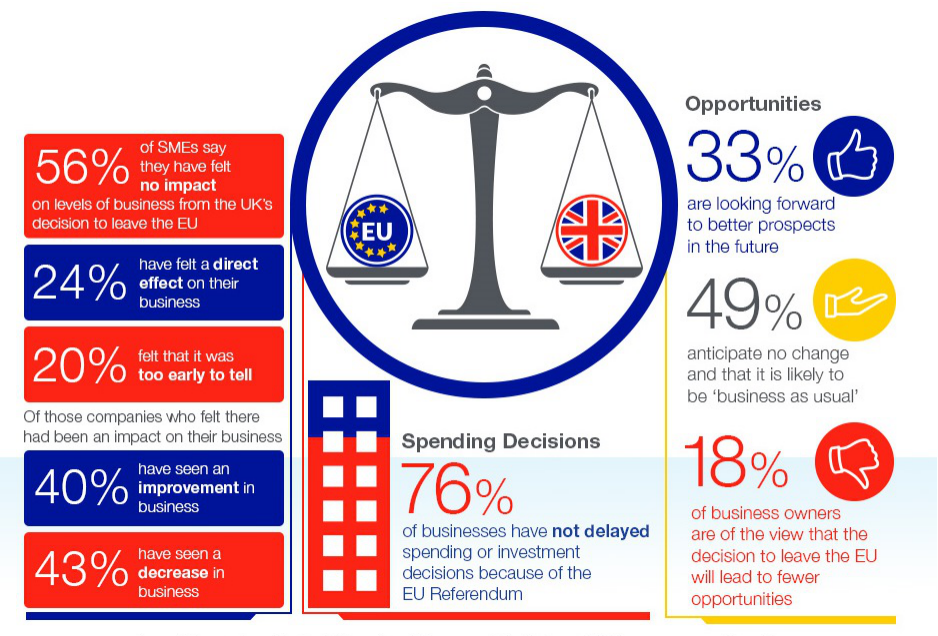
Illustration 1: UK SME’s
(Source: UK SME employees voice job security concerns following Brexit vote, 2016)
SMEs of UK are emerging and developing economy by seizing growth opportunities thereby addressing low productivity development and income gaps. SME’s and young firms are experiencing a rapid growth in UK’s economy after Brexit as well, which is diverse in terms of business model, size, performance and aspirations ( Ryu and Kim, 2018). According to the major economic survey conducted over some 1000 SMEs reveals chances of uncertainties that might affect these businesses in their future strategic decisions.
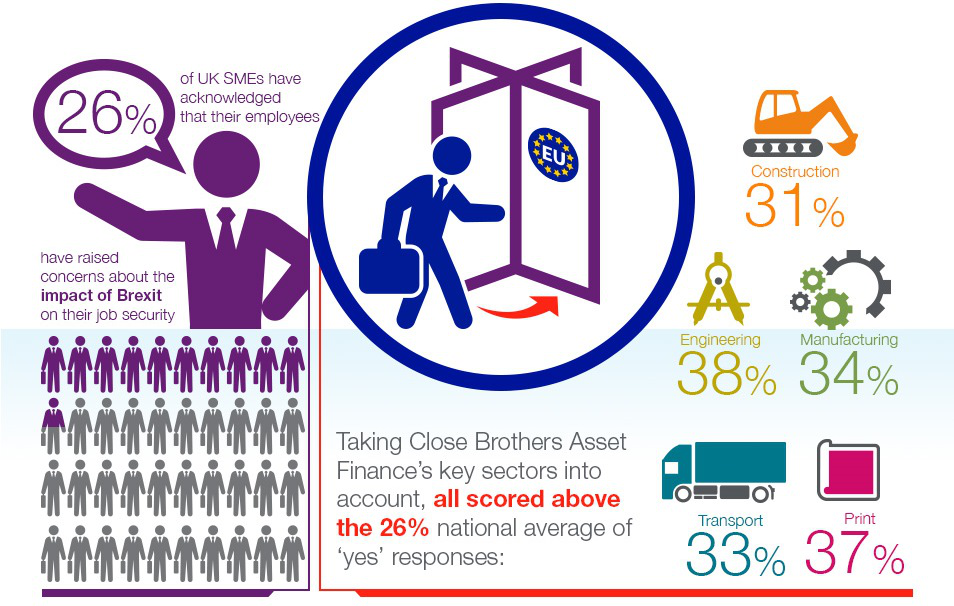
Illustration 2: UK SME’s
(Source: UK SME employees voice job security concerns following Brexit vote, 2016)
Small and mid-sized businesses of UK have become more concentrated on to domestic market as every regional markets have seen a decline in business since Brexit yet it had no direct impact on them. The government and industry have an important role in developing networks and support backing to encourage optimistic SME’s (Rana and Nipa, 2019). The European Commission considers SME’s as crucial factor that renders economic growth, innovation, job creation and social integration. Micro firms, young, innovative and high growth SME’s and some entrepreneurs including women business owners are putting a cross cutting approach to SME policies to enhance contributions to wide-ranging growth and strengthening to adapt major transformations.
SME’s including microenterprises have played an important role in fostering growth, employment and income of people in UK thereby being an integral part to the country’s economic transformation. According to the federation of small businesses, SME’s employs 15.6 million people producing a turnover of £1.75 trillion. These growing companies have a huge impact on the UK’s economy as these are creating more jobs of around 238,000 and £38 billion gross value within three years.
M2 Define the medium and large businesses
|
Medium businesses |
Large Businesses |
|
They are the middle level business enterprise with a work force of about 250 employees. |
They are the enterprise with an employee count of more than 250 workers. |
|
They are the largest employer and are present in a significant number. |
They are also one of the larget empl;oyer on local and international level but are few in numbers. |
|
They form out a larger part of overall GDP of a country and have a wide range of industries falling within it. |
They are major tax payer firms and usually work in manufacturing and production sector. |
|
They usually operate on local and intercity or state level. |
They operate on national and international level. |
Both the firms have the significant role on the economy of a nation. While medium level firms are the largest employer and supports in reducing unemployable rate, larger firm have higher profits and thus, constitute a major part of economy and GDP of a country. They have a huge impact on the economy by increasing financial stability, getting foreign investment, improving trade relations with the firm and catalysing the economic growth of an organisation.
D2 Growth and development of small, medium and large level firms on local, regional, national and international level
The SME and large enterprises will help in proper assessment of business operations and thus will lead the firm to have a good and effective growth of local, regional, national and global level. These firms assist an organisation to meet their needs and thus will guide the organisation to improve performance level of an organisation. The accessing of wider customer needs, developing high quality product's and services. Besides this, it assists management of a business enterprise to get FDI and improve trade relations on global level by reducing lack of employability on local or regional level.
TASK 3
P5. Mini research to determine characteristics, traits and skills of two successful entrepreneurs, which differentiate them from other business managers
Entrepreneurial characteristics are diverse and numerous which are mandatory for an entrepreneur to possess before starting their business (Nikolaou, Tasopoulou and Tsagarakis, 2018). These individualities help them in developing innovative ideas, bearing risks to make profits out of business thereby being successful. Oprah Winfrey and Jeff Bezoz are two entrepreneurs who have achieved success through managing business and prospered as business owners. Following are the characteristics, traits and skills of these efficacious business magnates:
OPRAH WINFREY
Oprah Winfrey is an American actor, talk show host and philanthropist who is the richest African American and first black multi-billionaire of North America. She is often known as the most influential women in the world.
Characteristics and Traits
Emotionally intelligent: Oprah Winfrey’s consciousness of her vision has led her to achieve great success with her listening skills and empathy that enabled to motivate others.
Inspirational: Oprah focuses on being the best person she can be by providing advices and suggestions to people in hard times.
Humanist: Oprah is a caring and empathetic individual who does not take justice and humanitarian issues carelessly. She has proven the power of a strong leader to positively influence lives of many.
Skills
Motivational: Oprah is the most inspirational and enthusiastic women who have been awarded with presidential Medal of Freedom. Oprah does not believe in failures rather she considers them as stepping-stones to success.
Adaptable: Oprah endured failure in her 20s as she was fired from her anchoring position and went through humiliating experiences doing lesser jobs.
JEFF BEZOZ
Jeff Bezoz is the founder of Amazon.com who holds a net worth of $159.6 billion making him richest person in world. He is an American technology entrepreneur, investor and philanthropist.
Characteristics and Traits
Ambitious: Jeff Bezoz strives for success and responds positively to others who are interested in the same ambitious activities. That desire of this entrepreneur is visible as he built a wealth of more than $100 billion and is world’s first trillionaire.
Persuasive: He is instant and swaying in building rapport with other people, which has made the society value his opinions about things. Jeff shows a loyal attitude while interacting with people that helps in building a long-term connection with them (Lipset, 2018 Morris and et.al., 2018).
Diligence: Bezoz is not obsessed despite of having strong ambition and adventurous spirit. He is good at following daily responsibilities making sure things do not fall through flaws.
Skills
Commitment: Bezoz and his venture focus on staying for long-term as a result, all decisions are taken in that context. Though amazon have experienced countless struggles to be established, Bezoz stayed committed and focused to the vision.
Focus: He stresses more on processes rather on failures, which are necessary to translate great fresh insights into new markets. Bezoz have the courage to fail and learn from failures by being focused on to the goal.
P6. Aspects of entrepreneurial personality that reflect entrepreneurial motivation and mind-set
Entrepreneurial personality included characteristics, capabilities, skills motives, attitudes and values, which help in developing individual’s experience and actions. It is the combination of several qualities, which form character of individuals. Integration of motives and different personality traits make it possible for entrepreneurs to advance their mind-set. Businessperson has the ability to carry out innovation in business and has a will to change with behaviour of passive adaptive (Julien, 2018).
BIG FIVE MODEL
Big five personality traits or the five factor model (FFM) and the OCEAN model is the classification of personality traits which uses common language descriptors to describe human behaviour. It helps individual make up an overall personality because of the underlying traits. The five factors are:
Openness to experience: It reflects the degree of intellectual curiosity, creativity for novelty a person has. Jeff Bezoz is open minded and imaginative and depicts a personal preference for variety of activities over a routine. Whereas, Oprah is a person with low openness that makes her to gain fulfilment through perseverance and are characterised as pragmatic.
Conscientiousness: Jeff Bezoz has the tendency to be organized and dependable showing his self-discipline, aim for achievement and planned spontaneous behaviour. Oprah has also a low conscientiousness with flexibility and spontaneity.
Extraversion: Oprah is energetic, assertive and sociable. Jeff Bezoz and Winfrey both are dominant and extroverted people in social settings.
Agreeableness: Jeff Bezoz and Oprah are compassionate and cooperative rather than suspicious and antagonistic to others. It measures trusting and helping nature of a person. Both entrepreneurs are involved in charity and donations to help people who are actually in need.
Neuroticism: It is the tendency to be prone to psychological stress, unpleasant emotions like anger, anxiety and depression. Oprah has the degree of emotional stability and impulse control which she has developed through her bad experiences. Jeff has low stability and is a reactive and excitable personality making him a dynamic person.
On the basis of this assessment, this can be concluded that these entrepreneurs are usually self motivated and work according to their plans and strategies and thus, will lead them to achieve their goals and objectives. They have an open and positive mindset, which encourages them to develop the strategies and thus will lead the firm to improve quality of services in much effective way. Their determination, passion, innovative ideology and skill sets are few factors which set them apart from the managers and help in improving theuir motivational level and skill sets.
M3 Examine the arguments such as “Can characteristics be learnt and adopted by anyone”
The skill sets and qualities that are been possessed by an entrepreneur are few of the qualities which helps the firm to improve the quality of services and action plans that are been taken by the entrepreneurial venture to have good growth and development. The statement “Can characteristics be learnt and adopted by anyone” is true to some extent as the qualities like determination, assessment of opportunities and other important traits can be learnt or adopted by an entrepreneur through learning or training. These characteristics and action plans will help the individual to have certain specific qualities which will enhance their performance to a higher level.
D3 Analyse the characteristic traits, skills and motivational drivers of successful entrepreneurs
Certain traits, motivation drivers and qualities like hard work, specialization in the respective field, honesty are few factors that are been taken in consideration that are taken in consideration by successful entrepreneurs mentioned above. These skill sets and motivational drivers are few factors that encourage an enterprise to set up his/ her enterprise and take calculated risks to convert business idea into successful enterprise.
TASK 4
P7. Background and experience which may hinder or foster entrepreneurship
Entrepreneurs experiences many phases in their life that might hinder or foster them in achieving success or setting up of entrepreneurial venture (Frederick, O'Connor and Kuratko, 2018 ). Background and experiences play a major role in shaping an entrepreneur, which includes factors like environment, society, education, childhood, family support etc.
Oprah Winfrey
Oprah was born in Kosciusko, Mississippi to an unmarried teenage mother and left in the care of maternal grandmother on farm. She led a difficult childhood with poor urban lifestyle, which had its negative effect on her as a young teenager. Oprah hosted the TV Chat Show in 1976 after moving to Baltimore, which became a hit where her success started. In 1986, Winfrey launched The Oprah Winfrey Show as a nationally syndicated program that grossed $125 million in its first year. (Aquino, Lück and Schänzel, 2018). The miseries and bad experiences would have made her fall into wrong ways but with her strong will power, adaptability and confidence Oprah was able to cope up with disappointments. As she had experienced the pain and griefs which has made her to become a humanist and help people who are facing hard times by motivating and rendering assistance as a philanthropist. The hard times which she experienced nurtured entrepreneurial characteristics of Oprah that made her a successful entrepreneur.
Jeff Bezoz
Jeff Bezoz was born in Albuquerque, New Mexico to a teenage mother. He showed early interests in how thing work by turning his parent’s garage into a laboratory. He developed love for computers and graduated with a degree in computer science and electrical engineering. He opened Amazon.com in 1995, which gave an initial success where the firm sold books around 45 countries, and sales reached $20,000 a week (Ahmadian and Abdolmaleki, 2018). Jeff was ambitious and had inborn talents, which helped him to achieve the success, which Amazon.com is enjoying today. His strong commitment, focus and educational knowledge made him reach to his level of success. The entrepreneurial traits including his education, skills helped Bezoz in establishing a venture and become a successful entrepreneur.
M4 Analyse the link between entrepreneurial characteristics and the influence of personal background
The entrepreneurial characteristics like honesty, specialisation and improvement of business operations are deeply linked with personal background and upbringing of an entrepreneur. A good personal knowledge and improved skill sets are key driving factors that assist an organisation to improve quality of services offered by a person. A supportive personal background, knowledge and skill sets with significant entrepreneurial characteristics will help in suitable establishing of an enterprise within a firm.
D4 Critically evaluate how background and experience influences entrepreneurs, both positively and negatively
Some traits and qualities that are taken in consideration by an entrepreneur will help the firm to improve their qualities and operations in much suitable way. On the positive side, it will improve their change to be successfully setting up their enterprise and generate good revenue. However, on negative part, this makes a person or entrepreneur more specified and peculiar, affecting their relationship with others and influencing their performance.
CONCLUSION
Study on entrepreneurship and small business management concludes that it is important for an entrepreneur to have entrepreneurial capabilities to manage their own start-up or business successfully. In addition, the report analysed several types of entrepreneurial ventures and their typologies to choose the right ones. It also discussed the similarities and differences between entrepreneurial ventures. The report summon that entrepreneur's family background, education and experience sets their decision making and mindsets which makes them distinct from business manager.
REFERENCES
- Akehurst, G., Simarro, E. and Mas‐Tur, A., 2012. Women entrepreneurship in small service firms: Motivations, barriers and performance. The Service Industries Journal. 32(15). pp.2489-2505.
- Alsos, G.A., Carter, S. and Ljunggren, E. eds., 2011. The handbook of research on entrepreneurship in agriculture and rural development. Edward Elgar Publishing.
- Blackburn, R.A., Hart, M. and Wainwright, T., 2013. Small business performance: business, strategy and owner-manager characteristics. Journal of small business and enterprise development. 20(1). pp.8-27.
- Dunn, P. and Liang, K., 2011. A COMPARISON OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP/SMALL BUSINESS AND FINANCE PROFESSORS'REACTION TO SELECTED ENTREPRENEURIAL AND SMALL BUSINESS FINANCIAL PLANNING AND MANAGEMENT ISSUES. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education. 14. p.93.
- Fayolle, A. and Gailly, B., 2015. The impact of entrepreneurship education on entrepreneurial attitudes and intention: Hysteresis and persistence. Journal of Small Business Management. 53(1). pp.75-93.



















